-
 Iran orders talks with US as Trump warns of 'bad things' if no deal reached
Iran orders talks with US as Trump warns of 'bad things' if no deal reached
-
From 'watch his ass' to White House talks for Trump and Petro

-
 Liverpool seal Jacquet deal, Palace sign Strand Larsen on deadline day
Liverpool seal Jacquet deal, Palace sign Strand Larsen on deadline day
-
Trump says not 'ripping' down Kennedy Center -- much

-
 Sunderland rout 'childish' Burnley
Sunderland rout 'childish' Burnley
-
Musk merges xAI into SpaceX in bid to build space data centers

-
 Former France striker Benzema switches Saudi clubs
Former France striker Benzema switches Saudi clubs
-
Sunderland rout hapless Burnley

-
 Costa Rican president-elect looks to Bukele for help against crime
Costa Rican president-elect looks to Bukele for help against crime
-
Hosts Australia to open Rugby World Cup against Hong Kong

-
 New York records 13 cold-related deaths since late January
New York records 13 cold-related deaths since late January
-
In post-Maduro Venezuela, pro- and anti-government workers march for better pay

-
 Romero slams 'disgraceful' Spurs squad depth
Romero slams 'disgraceful' Spurs squad depth
-
Trump urges 'no changes' to bill to end shutdown

-
 Trump says India, US strike trade deal
Trump says India, US strike trade deal
-
Cuban tourism in crisis; visitors repelled by fuel, power shortages

-
 Liverpool set for Jacquet deal, Palace sign Strand Larsen on deadline day
Liverpool set for Jacquet deal, Palace sign Strand Larsen on deadline day
-
FIFA president Infantino defends giving peace prize to Trump

-
 Trump cuts India tariffs, says Modi will stop buying Russian oil
Trump cuts India tariffs, says Modi will stop buying Russian oil
-
Borthwick backs Itoje to get 'big roar' off the bench against Wales

-
 Twenty-one friends from Belgian village win €123mn jackpot
Twenty-one friends from Belgian village win €123mn jackpot
-
Mateta move to Milan scuppered by medical concerns: source

-
 Late-January US snowstorm wasn't historically exceptional: NOAA
Late-January US snowstorm wasn't historically exceptional: NOAA
-
Punctuality at Germany's crisis-hit railway slumps

-
 Gazans begin crossing to Egypt for treatment after partial Rafah reopening
Gazans begin crossing to Egypt for treatment after partial Rafah reopening
-
Halt to MSF work will be 'catastrophic' for people of Gaza: MSF chief

-
 Italian biathlete Passler suspended after pre-Olympics doping test
Italian biathlete Passler suspended after pre-Olympics doping test
-
Europe observatory hails plan to abandon light-polluting Chile project

-
 Iran president orders talks with US as Trump hopeful of deal
Iran president orders talks with US as Trump hopeful of deal
-
Uncertainty grows over when US budget showdown will end

-
 Oil slides, gold loses lustre as Iran threat recedes
Oil slides, gold loses lustre as Iran threat recedes
-
Russian captain found guilty in fatal North Sea crash

-
 Disney earnings boosted by theme parks, as CEO handover nears
Disney earnings boosted by theme parks, as CEO handover nears
-
Sri Lanka drop Test captain De Silva from T20 World Cup squad

-
 France demands 1.7 bn euros in payroll taxes from Uber: media report
France demands 1.7 bn euros in payroll taxes from Uber: media report
-
EU will struggle to secure key raw materials supply, warns report

-
 France poised to adopt 2026 budget after months of tense talks
France poised to adopt 2026 budget after months of tense talks
-
Latest Epstein file dump rocks UK royals, politics

-
 Arteta seeks Arsenal reinforcement for injured Merino
Arteta seeks Arsenal reinforcement for injured Merino
-
Russia uses sport to 'whitewash' its aggression, says Ukraine minister

-
 Chile officially backs Bachelet candidacy for UN top job
Chile officially backs Bachelet candidacy for UN top job
-
European stocks rise as oil tumbles, while tech worries weigh on New York

-
 England captain Itoje on bench for Six Nations opener against Wales
England captain Itoje on bench for Six Nations opener against Wales
-
Rahm says golfers should be 'free' to play where they want after LIV defections

-
 More baby milk recalls in France after new toxin rules
More baby milk recalls in France after new toxin rules
-
Rosenior will not rush Estevao return from Brazil

-
 Mercedes ready to win F1 world title, says Russell
Mercedes ready to win F1 world title, says Russell
-
Germany hit by nationwide public transport strike

-
 Barca coach Flick 'not happy' with Raphinha thigh strain
Barca coach Flick 'not happy' with Raphinha thigh strain
-
WHO chief says turmoil creates chance for reset


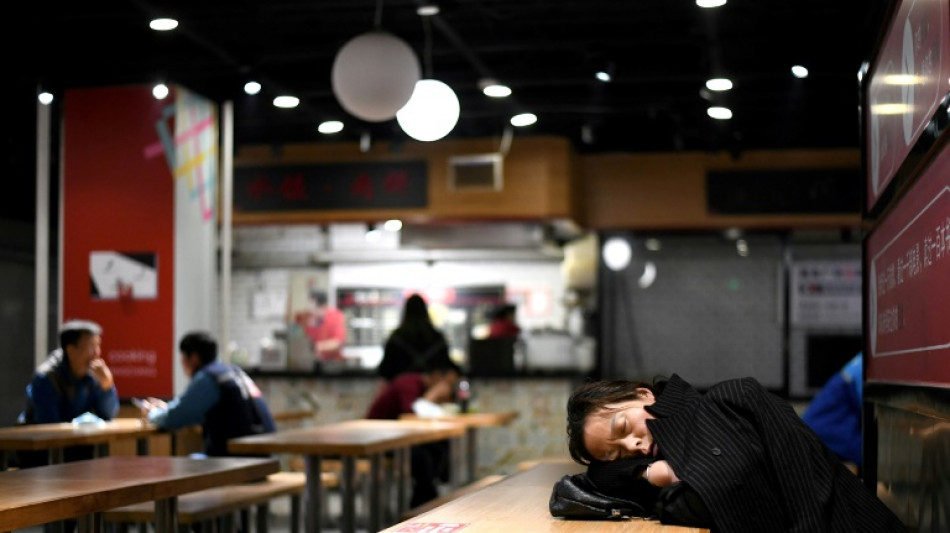
Science of sleep: Why a good night's rest gets harder with age
It's well known that getting a good night's sleep becomes more difficult as we age, but the underlying biology for why this happens has remained poorly understood.
A team of US scientists has now identified how the brain circuitry involved in regulating sleepfulness and wakefulness degrades over time in mice, which they say paves the way for better medicines in humans.
"More than half of people 65 and older complain about the quality of sleep," Stanford University professor Luis de Lecea, who co-authored a study about the finding published Thursday in Science, told AFP.
Research has shown that sleep deprivation is linked to an increased risk of multiple poor health outcomes, from hypertension to heart attacks, diabetes, depression and a build up of brain plaque linked to Alzheimer's.
Insomnia is often treated with a class of drugs known as hypnotics, which include Ambien, but these don't work very well in the elderly population.
For the new study, de Lecea and colleagues decided to investigate hypocretins, key brain chemicals that are generated only by a small cluster of neurons in the brain's hypothalamus, a region located between the eyes and ears.
Of the billions of neurons in the brain, only around 50,000 produce hypocretins.
In 1998, de Lecea and other scientists discovered that hypocretins transmit signals that play a vital role in stabilizing wakefulness.
Since many species experience fragmented sleep as they grow old, it's hypothesized that the same mechanisms are at play across mammals, and prior research had shown degradation of hypocretins leads to narcolepsy in humans, dogs and mice.
The team selected young (three to five months) and old mice (18 to 22 months) and used light carried by fibers to stimulate specific neurons. They recorded the results using imaging techniques.
What they found was that the older mice had lost approximately 38 percent of hypocretins compared to younger mice.
They also discovered that the hypocretins that remained in the older mice were more excitable and easily triggered, making the animals more prone to waking up.
This might be because of the deterioration over time of "potassium channels," which are biological on-off switches critical to the functions of many types of cells.
"The neurons tend to be more active and fire more, and if they fire more, you wake up more frequently," said de Lecea.
Identifying the specific pathway responsible for sleep loss could lead to better drugs, argued Laura Jacobson and Daniel Hoyer, of Australia's Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health, in a related commentary article.
Current treatments, such as hypnotics, "can induce cognitive complaints and falls," and medicines that target the specific channel might work better, they said.
These will need to be tested in clinical trials -- but an existing drug known as retigabine, which is currently used to treat epilepsy and which targets a similar pathway -- could be promising, said de Lecea.
F.Müller--BTB