-
 Giannis suitors make deals as NBA trade deadline nears
Giannis suitors make deals as NBA trade deadline nears
-
Carrick stresses significance of Munich air disaster to Man Utd history

-
 Record January window for transfers despite drop in spending
Record January window for transfers despite drop in spending
-
'Burned inside their houses': Nigerians recount horror of massacre

-
 Iran, US prepare for Oman talks after deadly protest crackdown
Iran, US prepare for Oman talks after deadly protest crackdown
-
Winter Olympics opening ceremony nears as virus disrupts ice hockey

-
 Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
-
Davos forum opens probe into CEO Brende's Epstein links

-
 ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
-
Famine spreading in Sudan's Darfur, warn UN-backed experts

-
 Lights back on in eastern Cuba after widespread blackout
Lights back on in eastern Cuba after widespread blackout
-
Russia, US agree to resume military contacts at Ukraine talks

-
 Greece aims to cut queues at ancient sites with new portal
Greece aims to cut queues at ancient sites with new portal
-
No time frame to get Palmer in 'perfect' shape - Rosenior

-
 Stocks fall as tech valuation fears stoke volatility
Stocks fall as tech valuation fears stoke volatility
-
US Olympic body backs LA28 leadership amid Wasserman scandal

-
 Gnabry extends Bayern Munich deal until 2028
Gnabry extends Bayern Munich deal until 2028
-
England captain Stokes suffers facial injury after being hit by ball

-
 Italy captain Lamaro amongst trio set for 50th caps against Scotland
Italy captain Lamaro amongst trio set for 50th caps against Scotland
-
Piastri plays down McLaren rivalry with champion Norris

-
 ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
-
Spain, Portugal face floods and chaos after deadly new storm

-
 EU close to sealing trade deal with Australia
EU close to sealing trade deal with Australia
-
German Cup final to stay in Berlin until 2030

-
 What does Iran want from talks with the US?
What does Iran want from talks with the US?
-
Taming the lion: Olympians take on Bormio's terrifying Stelvio piste

-
 Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
-
Italy's Casse tops second Olympic downhill training

-
 Anti-doping boss 'uncomfortable' with Valieva's coach at Olympics
Anti-doping boss 'uncomfortable' with Valieva's coach at Olympics
-
Bitcoin under $70,000 for first time since Trump's election

-
 'I am sorry,' embattled UK PM tells Epstein victims
'I am sorry,' embattled UK PM tells Epstein victims
-
England's Brook predicts record 300-plus scores at T20 World Cup

-
 Ukraine, Russia swap prisoners, US says 'work remains' to end war
Ukraine, Russia swap prisoners, US says 'work remains' to end war
-
Wales' Rees-Zammit at full-back for Six Nations return against England

-
 Sad horses and Draco Malfoy: China's unexpected Lunar New Year trends
Sad horses and Draco Malfoy: China's unexpected Lunar New Year trends
-
Hong Kong students dissolve pro-democracy group under 'severe' pressure

-
 Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
-
Germany claws back 70 mn euros from Amazon over price controls

-
 VW and Stellantis urge help to keep carmaking in Europe
VW and Stellantis urge help to keep carmaking in Europe
-
Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls

-
 BBVA posts record profit after failed Sabadell takeover
BBVA posts record profit after failed Sabadell takeover
-
UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief

-
 Greenpeace slams fossil fuel sponsors for Winter Olympics
Greenpeace slams fossil fuel sponsors for Winter Olympics
-
Greenpeace slams fossel fuel sponsors for Winter Olympics

-
 Kinghorn, Van der Merwe dropped by Scotland for Six Nations opener
Kinghorn, Van der Merwe dropped by Scotland for Six Nations opener
-
Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK

-
 Salt war heats up in ice-glazed Berlin
Salt war heats up in ice-glazed Berlin
-
Liverpool in 'good place' for years to come, says Slot

-
 Heathrow still Europe's busiest airport, but Istanbul gaining fast
Heathrow still Europe's busiest airport, but Istanbul gaining fast
-
Highest storm alert lifted in Spain, one woman missing


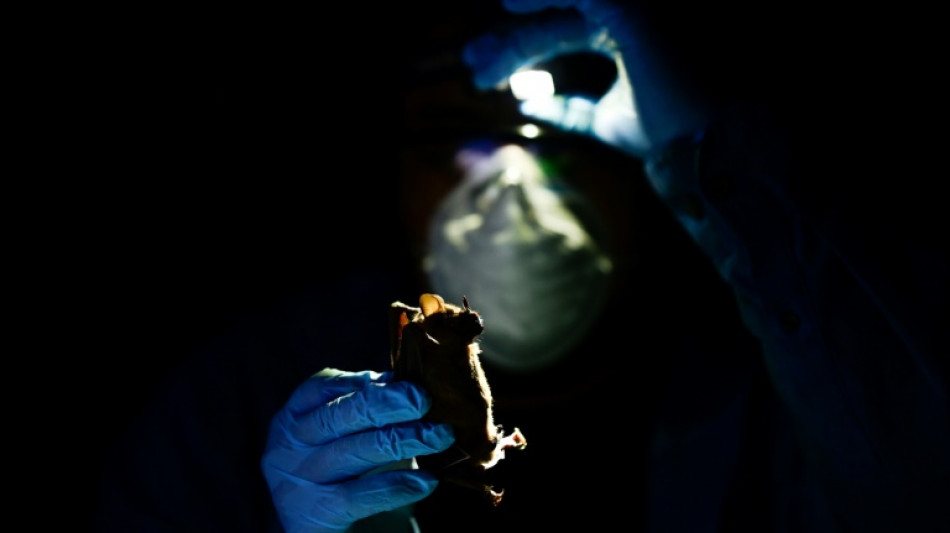
In Mexican jungle, scientists prepare for future pandemics
As night fell in Mexico's Yucatan jungle, veterinarian Omar Garcia extracted blood and fluids from a bat as part of an investigation aimed at preventing the next potential pandemic.
The goal of the Franco-Mexican project is to detect diseases -- known as zoonoses -- transmitted from animals to humans in tropical climates.
Bats are under scrutiny from the international scientific community as a possible source of coronavirus transmission.
The winged mammal remained immobile while bearing its fangs, before being released by Garcia, a vector-borne disease expert.
Scientists from France's Research Institute for Development (IRD) and the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) have been collaborating in the study since 2017, using a modern laboratory in Merida, the Yucatan state capital.
The aim is to discover how different viruses that circulate between animals such as mammals, birds and rodents, can potentially pass to humans, said Audrey Arnal, an infectious diseases expert at the IRD.
"This is zoonosis... understanding what the consequences of human contact with wildlife could be and then understanding what could be the next epidemic that can come out of nature," she told AFP.
Scientists take samples of all kinds of animals from the rich ecosystem of the tropical rainforest, where they have identified 61 species of mosquitoes.
"We have many questions" to try to "complete the history of the transmission cycle" of viruses, said UNAM biologist Maria Jose Tolsa, who after a decade of research finally feels that the importance of her work is recognized.
"A pandemic has serious consequences for health and the economy," she said.
- High-risk zone -
The area was chosen for the research because rapid deforestation has made it "a highly emblematic region in terms of zoonosis emergency risks," said Benjamin Roche, a specialist in ecology and evolutionary biology at the IRD.
It is estimated that between 500,000 and 800,000 viruses could affect humans, he added.
The risks grow with the expansion of agriculture and tourism, which increase contact between animals and humans, according to researchers.
Thousands of trees have been felled in the Yucatan Peninsula to build President Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador's flagship tourist rail project, the Mayan Train, scheduled to start operating in December.
The government says that it is offsetting the loss with a tree-planting program and the creation of the second-largest tropical rainforest reserve in the world after the Amazon.
The key is to achieve a balance between humans and nature, Arnal said.
"The population have to live, eat and develop their economy," she added.
The research is being carried out in 12 communities across the three states that make up the Yucatan Peninsula.
"In birds we've found species that have been identified as reservoirs for the West Nile virus or influenza," said Rosa Elena Sarmiento, from the virology laboratory of the UNAM Veterinary School.
- 'Great revealer' -
Field work begins at dawn by placing a dozen fine nets to trap birds. At dusk it is the turn of bats and even owls.
Once caught, blood, fluid and ectoparasite samples -- if they carry them -- are taken.
Scientists identify the animal, measure it, record the data and check its condition before releasing it.
Later the material is analyzed in the laboratory.
"DNA is a great revealer," Arnal said.
"With the blood of the mosquito we can determine which species or which animal was bitten," she added.
Blood samples will also be taken from local residents to determine if they carry any virus that came from an animal.
The project also includes consultations with communities to learn about their environmental and social problems, and encourage forms of coexistence with nature.
"There has to be a knowledge dialogue with the communities," said Erika Marce Santos, a member of the Mexican Association of Conservation Medicine who liaises with residents.
The Merida laboratory is connected with others in Africa, South Asia and other Latin American countries within the framework of an initiative called Preventing Zoonotic Disease Emergence.
Launched by France in 2022, it brings together 22 countries and 200 organizations.
"What we're looking for in the Yucatan is to devise a prevention strategy against zoonoses that can serve as an example to the whole world," Roche said.
O.Bulka--BTB




