-
 Fit-again France captain Dupont partners Jalibert against Ireland
Fit-again France captain Dupont partners Jalibert against Ireland
-
French summons Musk for 'voluntary interview' as authorities raid X offices

-
 IOC chief Coventry calls for focus on sport, not politics
IOC chief Coventry calls for focus on sport, not politics
-
McNeil's partner hits out at 'brutal' football industry after Palace move collapses

-
 Proud moment as Prendergast brothers picked to start for Ireland
Proud moment as Prendergast brothers picked to start for Ireland
-
Germany has highest share of older workers in EU

-
 Teen swims four hours to save family lost at sea off Australia
Teen swims four hours to save family lost at sea off Australia
-
Ethiopia denies Trump claim mega-dam was financed by US

-
 Norway crown princess's son pleads not guilty to rapes as trial opens
Norway crown princess's son pleads not guilty to rapes as trial opens
-
Russia resumes strikes on freezing Ukrainian capital ahead of talks

-
 Malaysian court acquits French man on drug charges
Malaysian court acquits French man on drug charges
-
Switch 2 sales boost Nintendo profits, but chip shortage looms

-
 China to ban hidden car door handles, setting new safety standards
China to ban hidden car door handles, setting new safety standards
-
Switch 2 sales boost Nintendo results but chip shortage looms

-
 From rations to G20's doorstep: Poland savours economic 'miracle'
From rations to G20's doorstep: Poland savours economic 'miracle'
-
Russia resumes strikes on freezing Ukrainian capital

-
 'Way too far': Latino Trump voters shocked by Minneapolis crackdown
'Way too far': Latino Trump voters shocked by Minneapolis crackdown
-
England and Brook seek redemption at T20 World Cup

-
 Coach Gambhir under pressure as India aim for back-to-back T20 triumphs
Coach Gambhir under pressure as India aim for back-to-back T20 triumphs
-
'Helmets off': NFL stars open up as Super Bowl circus begins

-
 Japan coach Jones says 'fair' World Cup schedule helps small teams
Japan coach Jones says 'fair' World Cup schedule helps small teams
-
Equities and precious metals rebound after Asia-wide rout

-
 Do not write Ireland off as a rugby force, says ex-prop Ross
Do not write Ireland off as a rugby force, says ex-prop Ross
-
Winter Olympics 2026: AFP guide to Alpine Skiing races

-
 Winter Olympics to showcase Italian venues and global tensions
Winter Olympics to showcase Italian venues and global tensions
-
Buoyant England eager to end Franco-Irish grip on Six Nations

-
 China to ban hidden car door handles in industry shift
China to ban hidden car door handles in industry shift
-
Sengun leads Rockets past Pacers, Ball leads Hornets fightback

-
 Waymo raises $16 bn to fuel global robotaxi expansion
Waymo raises $16 bn to fuel global robotaxi expansion
-
Netflix to livestream BTS comeback concert in K-pop mega event

-
 Rural India powers global AI models
Rural India powers global AI models
-
US House to vote Tuesday to end shutdown

-
 Equities, metals, oil rebound after Asia-wide rout
Equities, metals, oil rebound after Asia-wide rout
-
Bencic, Svitolina make history as mothers inside tennis top 10

-
 Italy's spread-out Olympics face transport challenge
Italy's spread-out Olympics face transport challenge
-
Son of Norway crown princess stands trial for multiple rapes

-
 Side hustle: Part-time refs take charge of Super Bowl
Side hustle: Part-time refs take charge of Super Bowl
-
Paying for a selfie: Rome starts charging for Trevi Fountain

-
 Faced with Trump, Pope Leo opts for indirect diplomacy
Faced with Trump, Pope Leo opts for indirect diplomacy
-
NFL chief expects Bad Bunny to unite Super Bowl audience

-
 Australia's Hazlewood to miss start of T20 World Cup
Australia's Hazlewood to miss start of T20 World Cup
-
Bill, Hillary Clinton to testify in US House Epstein probe

-
 Cuba confirms 'communications' with US, but says no negotiations yet
Cuba confirms 'communications' with US, but says no negotiations yet
-
Iran orders talks with US as Trump warns of 'bad things' if no deal reached

-
 From 'watch his ass' to White House talks for Trump and Petro
From 'watch his ass' to White House talks for Trump and Petro
-
Liverpool seal Jacquet deal, Palace sign Strand Larsen on deadline day

-
 Trump says not 'ripping' down Kennedy Center -- much
Trump says not 'ripping' down Kennedy Center -- much
-
Sunderland rout 'childish' Burnley

-
 Musk merges xAI into SpaceX in bid to build space data centers
Musk merges xAI into SpaceX in bid to build space data centers
-
Former France striker Benzema switches Saudi clubs


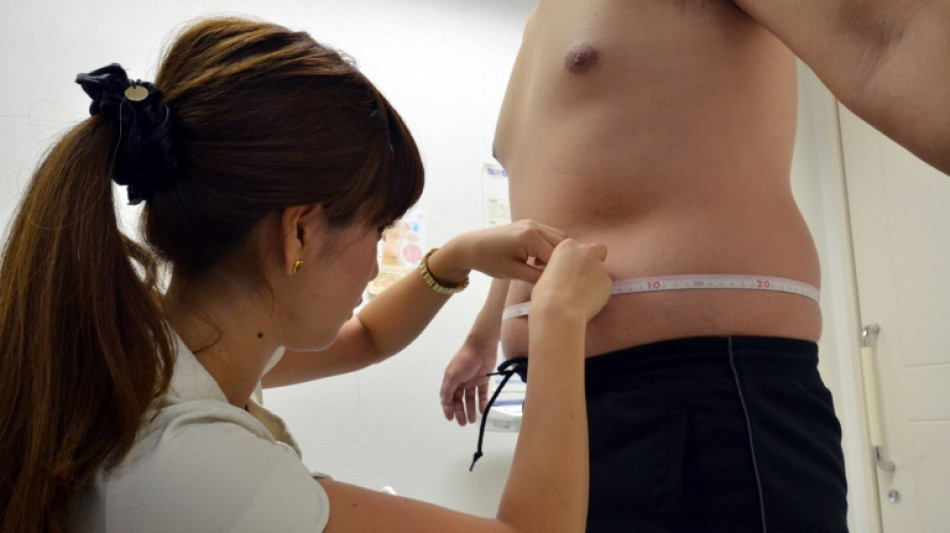
Is obesity a disease? Sometimes but not always, experts decide
Do people with obesity have an illness? A panel of global health experts looking at this controversial question announced Wednesday that the definition of obesity should be split into two categories -- and diagnosed using more accurate measurements.
The recommendations hoped to move past the blame and discrimination that often revolve around obesity, which is estimated to affect more than a billion people worldwide.
"The idea of obesity as a disease is at the centre of one of the most controversial and polarising debates in modern medicine," said a paper by the 56-expert commission in the Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology journal.
On one hand, obesity is known to lead to an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes, heart disease, some cancers and other health problems. This is why the World Health Organization among others consider it to be a "chronic complex disease".
On the other hand, there are also plenty of people defined as obese who have few or no underlying health problems and lead active, healthy lives. Activists campaigning against fat shaming, for example, do not want people with obesity to automatically be considered unwell.
At the same time, some patients and doctors believe obesity needs to be considered a disease so that it receives the attention -- and ambitious policy -- required for such a major public health issue.
Francesco Rubino, a bariatric surgeon and professor at King's College London who chaired the expert commission, told a press conference that the "controversy derives from the fact that perhaps not everybody is entirely right and not everybody is entirely wrong".
- Introducing 'clinical obesity' -
After years of debate, the commission sought a middle road, introducing two new categories for people with obesity.
When obesity affects the functions of people's organs, it should be considered a distinct illness called "clinical obesity," the commission said.
The criteria for diagnosing clinical obesity included heart, liver or breathing problems, high cholesterol, sleep apnoea, hip, knee or feet pain or other problems that affect people's daily lives.
People with obesity who do not have such problems should be considered to have "pre-clinical obesity", which merits monitoring but not medical intervention, therefore avoiding the risk of "overdiagnosis", the commission said.
To diagnose obesity in the first place, the experts also recommended healthcare workers move beyond body mass index (BMI), which measures the ratio between weight and height and is widely considered inadequate.
They urged other measurements including waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio or even bone density scans to get a more accurate diagnosis.
The experts emphasised that more research was needed to find out what percentage of people fell into their two new categories.
They also made no recommendations about the new generation of weight loss drugs such as Wegovy that have exploded in popularity since the commission was formed.
- Not everyone convinced -
Some researchers not involved in the commission welcomed the recommendations.
Tom Sanders, professor emeritus of nutrition and dietetics at King's College London, said that an official recognition of clinical obesity "would hopefully persuade lawmakers to regard it as a disability".
"This would have implications in terms of discrimination particularly in employment as well as the social stigma associated with the condition," he added.
While the nuanced recommendations aimed for consensus, they also risked satisfying neither side of the long-running debate.
Some groups that represent patients did not want to hear that obesity is not always a disease.
Anne-Sophie Joly, founder of France's National Collective of Obese Associations, called the recommendations "counterproductive", telling AFP the experts were disconnected from the "reality on the ground" in which patients with obesity do not receive adequate care.
Sceptics that obesity is ever a disease were also not satisfied.
Sylvie Benkemoun, a psychologist who leads France's Reflection Group on Obesity and being Overweight, told AFP the recommendations were "not enough, even if they have the merit of starting a discussion".
She expressed concern that the experts said little about the care given to patients with obesity -- and that the recommendations were unlikely to change much about the attitude of caregivers.
F.Pavlenko--BTB



