-
 UNESCO recognition inspires hope in Afghan artist's city
UNESCO recognition inspires hope in Afghan artist's city
-
Ukraine, Russia, US negotiators gather in Abu Dhabi for war talks

-
 WTO must 'reform or die': talks facilitator
WTO must 'reform or die': talks facilitator
-
Doctors hope UK archive can solve under-50s bowel cancer mystery

-
 Stocks swing following latest AI-fuelled sell-off on Wall St
Stocks swing following latest AI-fuelled sell-off on Wall St
-
Demanding Dupont set to fire France in Ireland opener

-
 Britain's ex-prince Andrew leaves Windsor home: BBC
Britain's ex-prince Andrew leaves Windsor home: BBC
-
Coach plots first South Africa World Cup win after Test triumph

-
 Spin-heavy Pakistan hit form, but India boycott risks early T20 exit
Spin-heavy Pakistan hit form, but India boycott risks early T20 exit
-
Japan eyes Premier League parity by aligning calendar with Europe

-
 Whack-a-mole: US academic fights to purge his AI deepfakes
Whack-a-mole: US academic fights to purge his AI deepfakes
-
Love in a time of war for journalist and activist in new documentary

-
 'Unprecedented mass killing': NGOs battle to quantify Iran crackdown scale
'Unprecedented mass killing': NGOs battle to quantify Iran crackdown scale
-
Seahawks kid Cooper Kupp seeks new Super Bowl memories

-
 Thousands of Venezuelans march to demand Maduro's release
Thousands of Venezuelans march to demand Maduro's release
-
AI, manipulated images falsely link some US politicians with Epstein

-
 Move on, says Trump as Epstein files trigger probe into British politician
Move on, says Trump as Epstein files trigger probe into British politician
-
Arteta backs Arsenal to build on 'magical' place in League Cup final

-
 Evil Empire to underdogs: Patriots eye 7th Super Bowl
Evil Empire to underdogs: Patriots eye 7th Super Bowl
-
UBS grilled on Capitol Hill over Nazi-era probe

-
 Guardiola 'hurt' by suffering caused in global conflicts
Guardiola 'hurt' by suffering caused in global conflicts
-
Marseille do their work early to beat Rennes in French Cup

-
 Colombia's Petro, Trump hail talks after bitter rift
Colombia's Petro, Trump hail talks after bitter rift
-
Trump signs spending bill ending US government shutdown

-
 Arsenal sink Chelsea to reach League Cup final
Arsenal sink Chelsea to reach League Cup final
-
Leverkusen sink St Pauli to book spot in German Cup semis

-
 'We just need something positive' - Monks' peace walk across US draws large crowds
'We just need something positive' - Monks' peace walk across US draws large crowds
-
Milan close gap on Inter with 3-0 win over Bologna

-
 No US immigration agents at Super Bowl: security chief
No US immigration agents at Super Bowl: security chief
-
NASA Moon mission launch delayed to March after test

-
 'You are great': Trump makes up with Colombia's Petro in fireworks-free meeting
'You are great': Trump makes up with Colombia's Petro in fireworks-free meeting
-
Spain to seek social media ban for under-16s

-
 X hits back after France summons Musk, raids offices in deepfake probe
X hits back after France summons Musk, raids offices in deepfake probe
-
LIV Golf events to receive world ranking points: official

-
 Russia resumes large-scale Ukraine strikes in glacial weather
Russia resumes large-scale Ukraine strikes in glacial weather
-
US House passes spending bill ending government shutdown

-
 US jet downs Iran drone but talks still on course
US jet downs Iran drone but talks still on course
-
UK police launching criminal probe into ex-envoy Mandelson

-
 US-Iran talks 'still scheduled' after drone shot down: White House
US-Iran talks 'still scheduled' after drone shot down: White House
-
Chomsky sympathized with Epstein over 'horrible' press treatment

-
 French prosecutors stick to demand for five-year ban for Le Pen
French prosecutors stick to demand for five-year ban for Le Pen
-
Russia's economic growth slowed to 1% in 2025: Putin

-
 Bethell spins England to 3-0 sweep over Sri Lanka in World Cup warm-up
Bethell spins England to 3-0 sweep over Sri Lanka in World Cup warm-up
-
Nagelsmann backs Ter Stegen for World Cup despite 'cruel' injury

-
 Homage or propaganda? Carnival parade stars Brazil's Lula
Homage or propaganda? Carnival parade stars Brazil's Lula
-
EU must be 'less naive' in COP climate talks: French ministry

-
 Colombia's Petro meets Trump after months of tensions
Colombia's Petro meets Trump after months of tensions
-
Air India inspects Boeing 787 fuel switches after grounding

-
 US envoy evokes transition to 'democratic' Venezuela
US envoy evokes transition to 'democratic' Venezuela
-
Syria govt forces enter Qamishli under agreement with Kurds


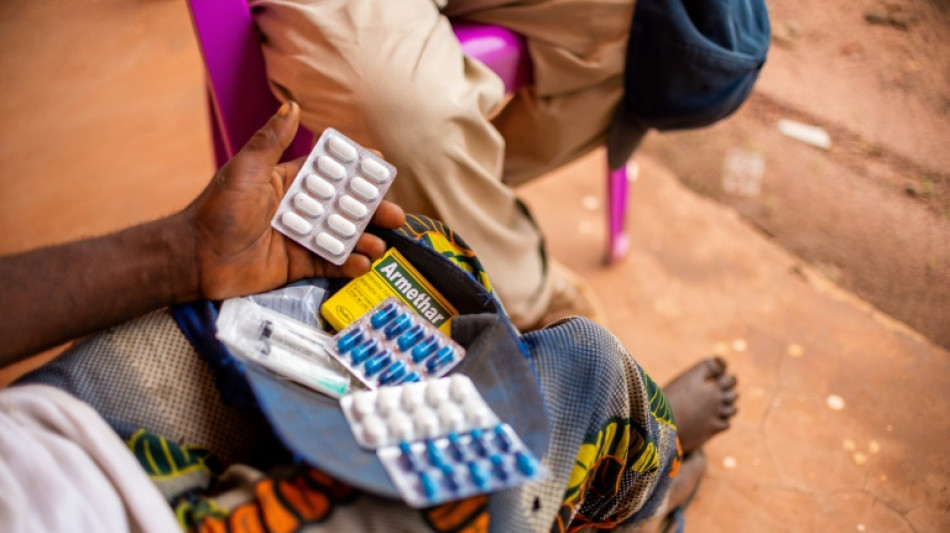
DR Congo drug manufacturing plan sparks safety concerns
Sitting at his desk overlooking a pharmaceutical factory floor on the outskirts of the Congolese capital Kinshasa, Joss Ilunga Dijimba, 52, cracked a jovial smile.
"It's not easy doing business in Congo," he said.
His family was forced to relocate the factory in the 1990s to survive bouts of mass looting. And nowadays, there are onerous taxes, customs duties, and problems retaining talented staff.
His company, which employs about 40 people and produces generics such as paracetamol, is one of a tiny number of drug manufacturers in the Democratic Republic of Congo, an impoverished nation roughly the size of Western Europe.
But a government plan to require hospitals and NGOs to buy more locally produced drugs could soon boost the fledgling pharmaceutical industry -- despite fears in some quarters that safety standards are far below international norms.
Several NGOs, some of which provide medical care in the DRC's conflict-torn east, have requested opt-outs.
At the small Pharmagros plant, behind barbed-wire walls near the Congo river, men in hairnets and white coats formulate medicines with imported precursor using lab equipment in airconditioned rooms.
"Promoting local industry's a good thing," said Dijimba, a University of Texas graduate, insisting that several Congolese firms, including his, maintained high standards.
"It could grow the middle class."
About 73 percent of the DRC's population of 90 million lives on under $1.9 a day, according to the World Bank. Most products in the African country are imported.
- 'At your own peril' -
The Congolese government has designated 35 drug molecules, including paracetamol, that medical facilities will be required to purchase in locally made form.
The government wants to stimulate business without banning imports, said Donatien Kabamb Kabey, the pharmaceuticals director at the DRC's health ministry.
He explained that all the molecules can be replaced with imported equivalents, suggesting that ibuprofen could replace paracetamol, for example.
Although not yet implemented, the policy already appears to be working.
Fifteen new pharma businesses are setting up in the DRC ahead of the new rules, Kabey said, which will add to the existing 24.
The policy was partly designed to encourage factories to return after fleeing the country in the 1990s, he added, when unpaid soldiers went on the rampage towards the end of ex-dictator Mobutu Sese Seko's reign.
But experts warn that Congolese-made medicines face a major challenge: reassuring doctors and patients that they meet regulatory standards.
"When you go to the private sector in Congo, you do it at your own peril," said Ed Vreeke, who runs the Belgium-based independent pharmaceutical auditing firm Quamed.
"They know darn well that the quality they produce is not good."
Vreeke said Congolese regulators had improved, but the country lacked the massive resources needed to properly perform audits, check labels, and inspect the chemical composition of drugs for safety.
Kabey, whose department at the health ministry oversees inspections, said standards had improved "enormously" in recent years, but did not provide further details.
He said the government was establishing a national quality-control lab.
- 'A huge thing' -
Shoddy or falsified medicines kill hundreds of thousands of people every year, according to the World Health Organization, mostly in poor countries.
The DRC's hot and humid climate also poses storage problems.
A 2021 study of both imported and locally produced eye drops sold in Kinshasa, for example, showed that three out of the seven products tested were substandard. The one sample manufactured in the DRC was contaminated.
Outside a pharmacy in Kinshasa's upmarket Gombe district, clutching a bag of medicines, 29-year-old corporate lawyer Joelle Mamputu said she didn't pay attention to where drugs were made but said she had "no prejudice".
However, a 52-year-old public servant named Olivier said there was "quite a difference" between Congolese and foreign drugs.
He added he would buy Congolese drugs were the quality the same.
Despite official assurances, major international NGOs such as Doctors Without Borders (MSF) and Medecins du Monde (MDM) have requested opt-outs from the purchasing requirements, several humanitarian workers said.
MSF declined to comment.
MDM confirmed it had asked for an exemption due to concerns over quality and capacity to meet demand.
"It's a huge thing," said one humanitarian who asked for anonymity, explaining that the new rules will affect all non-governmental organisations, hospitals and pharmacies.
Many aid workers understand the need to promote enterprise, he said, but there are internal disagreements about whether to compromise on quality.
"We need to have high quality standards for everyone, but the reality of the country is that sometimes it's impossible".
L.Janezki--BTB



