-
 Cuban tourism in crisis; visitors repelled by fuel, power shortages
Cuban tourism in crisis; visitors repelled by fuel, power shortages
-
Liverpool set for Jacquet deal, Palace sign Strand Larsen on deadline day

-
 FIFA president Infantino defends giving peace prize to Trump
FIFA president Infantino defends giving peace prize to Trump
-
Trump cuts India tariffs, says Modi will stop buying Russian oil

-
 Borthwick backs Itoje to get 'big roar' off the bench against Wales
Borthwick backs Itoje to get 'big roar' off the bench against Wales
-
Twenty-one friends from Belgian village win €123mn jackpot

-
 Mateta move to Milan scuppered by medical concerns: source
Mateta move to Milan scuppered by medical concerns: source
-
Late-January US snowstorm wasn't historically exceptional: NOAA

-
 Punctuality at Germany's crisis-hit railway slumps
Punctuality at Germany's crisis-hit railway slumps
-
Gazans begin crossing to Egypt for treatment after partial Rafah reopening

-
 Halt to MSF work will be 'catastrophic' for people of Gaza: MSF chief
Halt to MSF work will be 'catastrophic' for people of Gaza: MSF chief
-
Italian biathlete Passler suspended after pre-Olympics doping test

-
 Europe observatory hails plan to abandon light-polluting Chile project
Europe observatory hails plan to abandon light-polluting Chile project
-
Iran president orders talks with US as Trump hopeful of deal

-
 Uncertainty grows over when US budget showdown will end
Uncertainty grows over when US budget showdown will end
-
Oil slides, gold loses lustre as Iran threat recedes

-
 Russian captain found guilty in fatal North Sea crash
Russian captain found guilty in fatal North Sea crash
-
Disney earnings boosted by theme parks, as CEO handover nears

-
 Sri Lanka drop Test captain De Silva from T20 World Cup squad
Sri Lanka drop Test captain De Silva from T20 World Cup squad
-
France demands 1.7 bn euros in payroll taxes from Uber: media report

-
 EU will struggle to secure key raw materials supply, warns report
EU will struggle to secure key raw materials supply, warns report
-
France poised to adopt 2026 budget after months of tense talks

-
 Latest Epstein file dump rocks UK royals, politics
Latest Epstein file dump rocks UK royals, politics
-
Arteta seeks Arsenal reinforcement for injured Merino

-
 Russia uses sport to 'whitewash' its aggression, says Ukraine minister
Russia uses sport to 'whitewash' its aggression, says Ukraine minister
-
Chile officially backs Bachelet candidacy for UN top job

-
 European stocks rise as oil tumbles, while tech worries weigh on New York
European stocks rise as oil tumbles, while tech worries weigh on New York
-
England captain Itoje on bench for Six Nations opener against Wales

-
 Rahm says golfers should be 'free' to play where they want after LIV defections
Rahm says golfers should be 'free' to play where they want after LIV defections
-
More baby milk recalls in France after new toxin rules

-
 Rosenior will not rush Estevao return from Brazil
Rosenior will not rush Estevao return from Brazil
-
Mercedes ready to win F1 world title, says Russell

-
 Germany hit by nationwide public transport strike
Germany hit by nationwide public transport strike
-
Barca coach Flick 'not happy' with Raphinha thigh strain

-
 WHO chief says turmoil creates chance for reset
WHO chief says turmoil creates chance for reset
-
European stocks rise as gold, oil prices tumble

-
 Rink issues resolved, NHL stars chase Olympic gold at Milan
Rink issues resolved, NHL stars chase Olympic gold at Milan
-
S. Korea celebrates breakthrough K-pop Grammy win for 'Golden'

-
 Rodri rages that officials 'don't want' Man City to win
Rodri rages that officials 'don't want' Man City to win
-
Gaza's Rafah crossing makes limited reopening after two-year war

-
 African players in Europe: Ouattara dents Villa title hopes
African players in Europe: Ouattara dents Villa title hopes
-
Liverpool beat Chelsea to Rennes defender Jacquet - reports

-
 S. Korea celebrates breakthrough Grammy win for K-pop's 'Golden'
S. Korea celebrates breakthrough Grammy win for K-pop's 'Golden'
-
Trump says US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba

-
 Trump threatens legal action against Grammy host over Epstein comment
Trump threatens legal action against Grammy host over Epstein comment
-
Olympic Games in northern Italy have German twist

-
 Bad Bunny: the Puerto Rican phenom on top of the music world
Bad Bunny: the Puerto Rican phenom on top of the music world
-
Snapchat blocks 415,000 underage accounts in Australia

-
 At Grammys, 'ICE out' message loud and clear
At Grammys, 'ICE out' message loud and clear
-
Dalai Lama's 'gratitude' at first Grammy win

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.04% | 23.75 | $ | |
| RIO | 1.4% | 92.325 | $ | |
| CMSD | 0.15% | 24.085 | $ | |
| AZN | -1.86% | 186.965 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 0.12% | 82.5 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.57% | 61.025 | $ | |
| NGG | -1.03% | 84.4 | $ | |
| GSK | 1.42% | 52.345 | $ | |
| BCC | 1.28% | 81.86 | $ | |
| RYCEF | 4.19% | 16.7 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.3% | 25.783 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.53% | 13.15 | $ | |
| RELX | -0.75% | 35.535 | $ | |
| BP | -0.37% | 37.74 | $ | |
| VOD | 1.88% | 14.93 | $ |

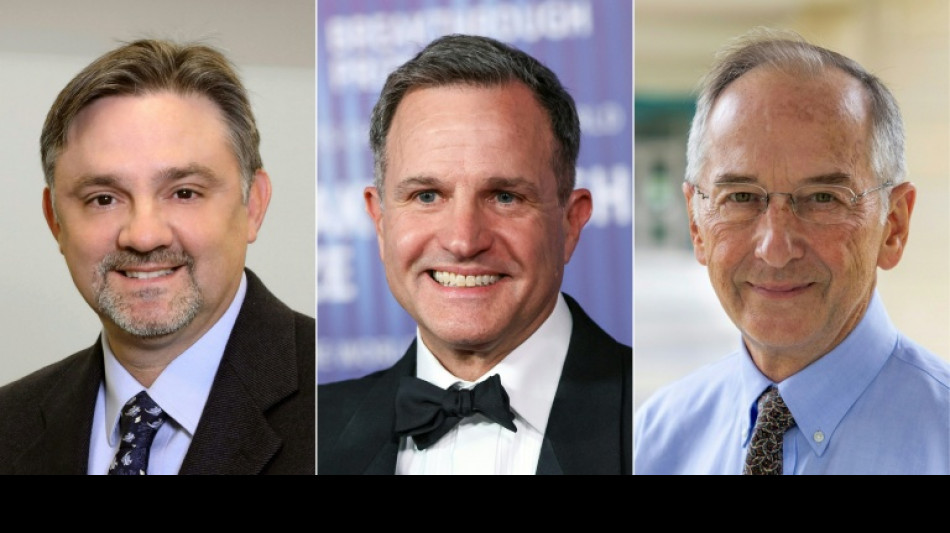
Scientists behind breakthrough cystic fibrosis treatment awarded top US prize
Cystic fibrosis was once a dire, likely deadly diagnosis, destroying a patient's ability to breathe and digest food -- but a revolutionary new treatment offers reason for hope.
And on Thursday the three scientists who developed the clinical advance were awarded America's most prestigious scientific award, taking home the Lasker prize.
The top honor is frequently cited as a pre-cursor for a potential Nobel, and this year it recognized the pulmonologist Michael Welsh along with researchers Jesus Gonzalez and Paul Negulescu from the US laboratory Vertex.
Their research has shed light on the causes of the disease and given rise to a new class of innovative drugs, including the flagship treatment Kaftrio -- known as Trikafta in the United States -- which are capable of stabilizing the otherwise debilitating condition.
"It's unbelievable. It's better than I ever hoped," Welsh told AFP. "You see these kids and they look healthy and they're not coughing. They're running around and playing."
"I almost can't believe it. Then they go, and they're getting married and they're having kids, and they're getting on with their lives."
That reality stands in sharp contrast to Welsh's memories from the early days of his career, when a cystic fibrosis diagnosis was a likely death sentence in childhood or adolescence.
The new award-winning treatment has been hailed as "revolutionary" by patient advocacy organizations.
It works by addressing the underlying causes of the inherited disease -- which wreaks havoc on the lungs and digestive system -- rather than its symptoms.
- 'Not totally broken' -
Some 100,000 people worldwide are estimated to suffer from cystic fibrosis, in which sticky mucus builds up in the lungs, digestive tract and other parts of the body.
After the 1989 discovery of the CFTR gene -- whose mutation was identified as the cause of the disease -- Welsh began dissecting the problem with fellow researchers.
"We thought, if we understand how CFTR works, we have a chance of fixing it," he said.
Gaining a better understanding of how the protein that the gene codes for led the pulmonologist down a path seeking how genetic mutations impaired its function.
Welsh identified two major anomalies caused by the most common mutation: a trapping of sorts of the protein within the cell, and its reduced performance.
The medical breakthrough resulted from experiments, notably some that showed how lowering temperature could help release the trapped protein.
"That meant it was not totally broken," Welsh remembered enthusiastically.
Armed with these discoveries, the American Cystic Fibrosis Foundation then approached researchers Gonzalez and Negulescu, who began studying the possibility of chemically reversing the identified malfunctions.
- 'Panning for gold' -
The notion of gene therapy -- which would aim to directly reverse the gene mutations -- had seemed on paper to be the simplest route.
But when it didn't work as hoped, patient organizations began to explore other options.
Gonzalez developed an innovative research technique using dyes that allowed for testing thousands of chemical compounds in record times.
"Without the screening, we would never have found these molecules," he said.
It was process akin to "panning for gold," recalled Negulescu.
But ultimately their dogged work paid off; they identified a handful of molecules that led to the birth of a new class of treatments.
Those molecules proved capable of restoring mobility to the stuck protein, and improving its function.
Kaftrio/Trikafta -- approved stateside in 2019 and classified by the World Health Organization as an essential treatment in 2025 -- is among them.
But their significant cost poses an obstacle for some patients, especially as the treatment is lifelong, and the therapy is ineffective in a small minority of patients including those with different mutations.
"The work is not done," said Negulescu.
P.Anderson--BTB