
-
 Voter swings raise midterm alarm bells for Trump's Republicans
Voter swings raise midterm alarm bells for Trump's Republicans
-
Australia dodges call for arrest of visiting Israel president

-
 Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
-
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation

-
 New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
-
Family affair: Thailand waning dynasty still election kingmaker

-
 Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
-
Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment

-
 LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
-
Ukraine, Russia, US to start second day of war talks

-
 Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
-
Trump attacks US electoral system with call to 'nationalize' voting

-
 Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
-
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy

-
 Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
-
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football

-
 On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
-
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting

-
 AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
-
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports

-
 Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
-
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world

-
 Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
-
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final

-
 Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
-
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist

-
 BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report

-
 Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through

-
 No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
-
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
-
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery

-
 Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
-
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
-
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum

-
 UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
-
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain

-
 Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
-
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act

-
 Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
-
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
-
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends

-
 Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
-
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses

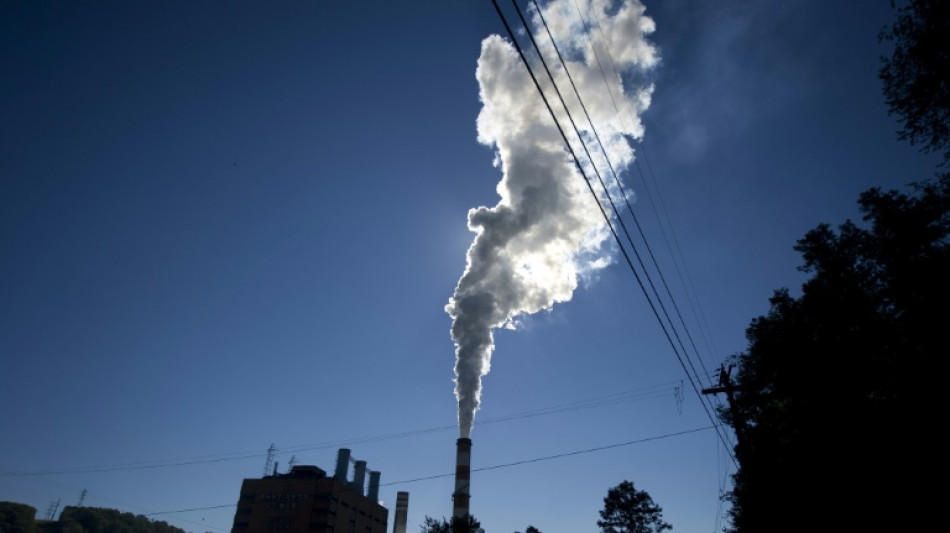
US moves to curb power plant emissions
President Joe Biden's administration on Thursday announced sweeping plans to curb planet-warming emissions from the nation's power stations, as part of the United States' efforts to combat the climate crisis.
Starting from 2030, the proposal would target fossil fuel electricity production with increasingly stringent carbon reduction requirements, including compelling some coal plants to directly capture pollution from their smokestacks.
"In every corner of our nation, Americans are seeing and feeling the devastating impacts of climate change," Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Administrator Michael Regan said at an event announcing the draft rules.
"It's clear that we've reached a pivotal point in human history, and it's on all of us to act right now to protect our future."
The agency estimated its measures targeting coal and natural gas would prevent 617 million metric tons of total carbon dioxide entering the atmosphere through 2042, equivalent to reducing the annual emissions of half the cars in the United States.
But the proposals are certain to face legal challenges from Republican-run states that could place them before the conservative-majority Supreme Court, which has previously knocked back efforts to regulate the sector.
US Senate Republican leader Mitch McConnell denounced the proposals, saying they posed "an existential threat to providers of affordable and reliable American energy."
US power plant emissions have been declining, thanks to a drop in the cost of renewables. But they are still responsible for a quarter of greenhouse gasses produced by the world's largest economy.
That has made it a prime target for Biden, who has pledged to cut emissions from electricity production to zero by 2035.
"I think this rule is important by declaring that the era of unlimited carbon pollution from power plants is over," Dan Lashof, director of World Resources Institute, United States, told AFP.
The proposed standards "mark a pivotal turning point," with the EPA "rightfully and necessarily moving to hold coal- and gas-fired power plants to account for their ongoing carbon pollution," added Julie McNamara of the Union of Concerned Scientists.
- Carbon capture -
Under the rules, measures for fossil fuel plants would vary by the type of plant, whether it operates frequently or just to shore up the grid during peak demand, and how long it is planned to remain in service.
For example, coal-fired plants that don't have commitments to retire by 2040 would be required to remove 90 percent of their carbon starting from 2030. On the other hand, coal plants set to retire by 2032 will face no restrictions.
Natural gas power stations that run frequently will be required to either implement carbon capture technology, or partly switch to hydrogen, which burns without emissions.
Both Lashof and McNamara said they had hoped for deeper and faster reductions for gas plants.
Boosting the use of carbon capture was slammed both by climate justice groups and the fossil fuel industry.
"If we are to combat climate change we must do so with real, viable solutions -- not unproven technologies that only promise to continue the legacy of dumping pollutants onto frontline communities," said Ozawa Bineshi Albert of the Climate Justice Alliance.
The National Mining Association said that although carbon capture was key to the future, mandating its use "before this technology is technically and fully economically demonstrated is nothing more than unlawful showmanship reinforcing a destructive agenda."
The technology is in its infancy, with only "around 35" facilities globally applying it for industrial processes, fuel transformation and power generation, according to the International Energy Agency.
But the Biden administration is betting on the Inflation Reduction Act, which offers tax credits for carbon capture, coupled with advances in the technology, to speed up adoption.
- Legally defensible? -
Former president Barack Obama first tried to regulate the power sector almost a decade ago, but the high court ruled his plans were too broad and exceeded the executive branch's authority.
The new rule limits itself to acting "within the fence line" of an individual power plant, which officials hope will improve its chances of surviving legal challenges.
The proposed rules come a month after the EPA unveiled new auto emissions regulations, and plans to sharply reduce emissions of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, by the oil and gas industry.
Biden, who faces a tough re-election campaign, sees keeping his promises on climate action as key to energizing younger voters.
The plans would be subject to a public comment period and likely wouldn't be finalized until next year.
O.Bulka--BTB



