
-
 Trump reinstates commercial fishing in protected Atlantic waters
Trump reinstates commercial fishing in protected Atlantic waters
-
Man Utd can't rush manager choice: Carrick

-
 Leeds boost survival bid with win over relegation rivals Forest
Leeds boost survival bid with win over relegation rivals Forest
-
Stars, Clydesdales and an AI beef jostle for Super Bowl ad glory

-
 Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
-
Freeski star Gu says injuries hit confidence as she targets Olympic treble

-
 UK police search properties in Mandelson probe
UK police search properties in Mandelson probe
-
Bompastor extends contract as Chelsea Women's boss despite slump

-
 Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with glittering ceremony
Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with glittering ceremony
-
A French yoga teacher's 'hell' in a Venezuelan jail

-
 England's Underhill taking nothing for granted against Wales
England's Underhill taking nothing for granted against Wales
-
Fans cheer for absent Ronaldo as Saudi row deepens

-
 Violence-ridden Haiti in limbo as transitional council wraps up
Violence-ridden Haiti in limbo as transitional council wraps up
-
Hundreds protest in Milan ahead of Winter Olympics

-
 Suspect in murder of Colombian footballer Escobar killed in Mexico
Suspect in murder of Colombian footballer Escobar killed in Mexico
-
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS Minnesota United

-
 Wainwright says England game still 'huge occasion' despite Welsh woes
Wainwright says England game still 'huge occasion' despite Welsh woes
-
WADA shrugs off USA withholding dues

-
 France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron
-
Winter Olympics to open with star-studded ceremony

-
 Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys
Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys
Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys
-
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United

-
 UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties
UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties
-
Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter

-
 US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests
US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests
-
French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut

-
 France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source
-
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles

-
 Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque
Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque
-
Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman

-
 US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
 Arteta apologises to Rosenior after disrespect row
Arteta apologises to Rosenior after disrespect row
-
Terror at Friday prayers: witness describes 'extremely powerful' blast in Islamabad

-
 Winter Olympics men's downhill: Three things to watch
Winter Olympics men's downhill: Three things to watch
-
Ice dancers Chock and Bates shine as US lead Japan in team event

-
 Stellantis takes massive hit on 'overestimation' of EV demand
Stellantis takes massive hit on 'overestimation' of EV demand
-
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer

-
 Spanish PM urges caution as fresh rain heads for flood zone
Spanish PM urges caution as fresh rain heads for flood zone
-
Iran says to hold more talks with US despite Trump military threats

-
 Russia accuses Kyiv of gun attack on army general in Moscow
Russia accuses Kyiv of gun attack on army general in Moscow
-
Cambodia reveals damage to UNESCO-listed temple after Thailand clashes

-
 Norway crown princess 'deeply regrets' Epstein friendship
Norway crown princess 'deeply regrets' Epstein friendship
-
Italy set for Winter Olympics opening ceremony as Vonn passes test

-
 England's Jacks says players back under-fire skipper Brook '100 percent'
England's Jacks says players back under-fire skipper Brook '100 percent'
-
Carrick relishing Frank reunion as Man Utd host Spurs

-
 Farrell keeps the faith in Irish still being at rugby's top table
Farrell keeps the faith in Irish still being at rugby's top table
-
Meloni, Vance hail 'shared values' amid pre-Olympic protests


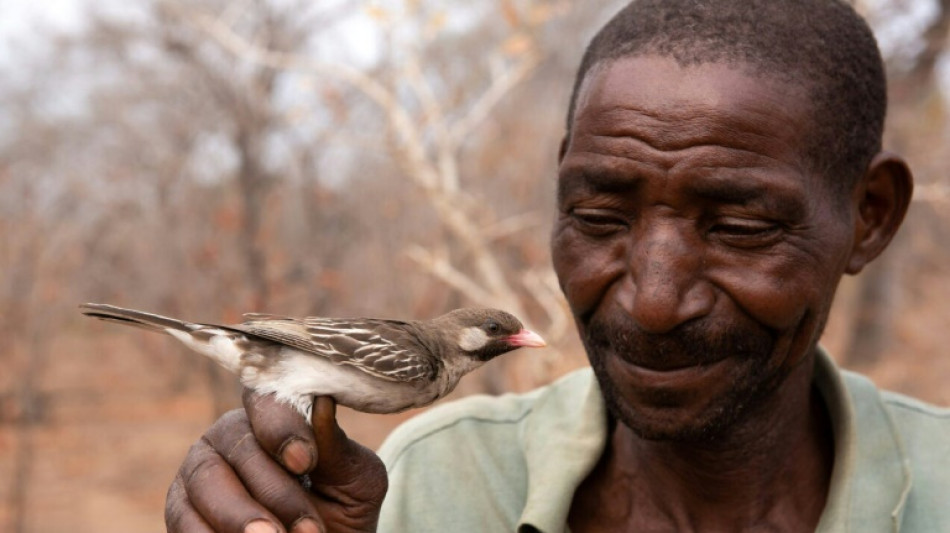
Wild birds analyze grunts, whistles made by human honey-hunters
In parts of Africa, expert honey-hunters call out to a species of bird known as the greater honeyguide, which leads them to wild bee nests -- a mutually beneficial practice.
In a new study published Thursday in Science, researchers have found that honeyguide birds in Tanzania and Mozambique distinguish between honey-hunters' calls, responding more readily to signals used in their local area.
"The assignment of meaning to arbitrary or semi-arbitrary sounds is one of the features that characterizes human language," joint lead author Claire Spottiswoode, an evolutionary biologist at the University of Cambridge, told AFP.
The new research shows this phenomenon "extends to our interactions with other species, showing how continuous we really are with the rest of the natural world."
The Hadza, a group of hunter-gatherers in northern Tanzania, use a melodic whistle to initiate a partnership with honeyguides, while the Yao people of Mozambique use a trill followed by a grunt that sounds like "brrr-hmm!"
Once a nest is found, the humans crack it open, harvesting the honey and bee larvae, while the birds feast on the exposed beeswax.
Using mathematical models and audio playback, Spottiswoode and her co-author Brian Wood, a UCLA anthropologist, studied these signals, how helpful they were for people, and their effects on the birds.
They found the honeyguide birds of Tanzania were more than three times more likely to cooperate after hearing local Hadza whistles compared to "foreign" Yao calls.
Conversely, the honeyguides of Mozambique were almost twice as likely to seek a partnership after hearing a Yao trill-grunt than a foreign Hadza whistle.
The authors called this an example of "cultural coevolution," with humans of an area more likely to be successful if they stick to the local tradition, just as the birds of that region keep their ears out for the specific local call.
As for why such stark differences arose between the communities, practical considerations may be at play.
The Hadza hunt mammals using bows and arrows, and using a bird-like whistle reduces the chances of frightening away the other prey they are also after.
The Yao, meanwhile, don't hunt mammals and their trill-grunt might be a good way of scaring off elephants or buffaloes whom they don't wish to startle in a close encounter.
"Not just among the Hadza, but in hunting cultures around the world, people use whistles as a form of encrypted communication -- to share information while avoiding detection by prey," Wood said.
- A dying practice -
How exactly honeyguides learn localized human calls is an area for future study.
Perhaps they watch and copy the behavior of older birds, or perhaps they form positive associations between the human signal and a reward.
Nor is it known just how far this partnership goes back.
Our pre-Homo sapien ancestors acquired mastery of fire and stone tools between 1.5 - 3 million years ago, respectively, and so "it's plausible that this relationship could be really ancient," said Spottiswoode.
It wasn't until a seminal study published in 1989 that the scientific world was convinced the honeyguide-honey hunter relationship was real, not just a folktale or superstition.
But the practice is slowly dying out, partly as a result of changes in the way people obtain sweet food, and partly because people are prevented from interacting with honeyguides in protected nature parks.
"The birds still call to us, but we don't necessarily follow them," said Spottiswoode.
"We should really treasure these remaining places where the relationship still thrives and where this rich interspecies culture still exists."
M.Odermatt--BTB


