
-
 Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United
-
UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties

-
 Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter
Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter
-
US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests

-
 French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut
French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut
-
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source

-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque

-
 Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman
Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman
-
US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested

-
 Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
Arteta apologises to Rosenior after disrespect row

-
 Terror at Friday prayers: witness describes 'extremely powerful' blast in Islamabad
Terror at Friday prayers: witness describes 'extremely powerful' blast in Islamabad
-
Winter Olympics men's downhill: Three things to watch

-
 Ice dancers Chock and Bates shine as US lead Japan in team event
Ice dancers Chock and Bates shine as US lead Japan in team event
-
Stellantis takes massive hit on 'overestimation' of EV demand

-
 Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
-
Spanish PM urges caution as fresh rain heads for flood zone

-
 Iran says to hold more talks with US despite Trump military threats
Iran says to hold more talks with US despite Trump military threats
-
Russia accuses Kyiv of gun attack on army general in Moscow

-
 Cambodia reveals damage to UNESCO-listed temple after Thailand clashes
Cambodia reveals damage to UNESCO-listed temple after Thailand clashes
-
Norway crown princess 'deeply regrets' Epstein friendship

-
 Italy set for Winter Olympics opening ceremony as Vonn passes test
Italy set for Winter Olympics opening ceremony as Vonn passes test
-
England's Jacks says players back under-fire skipper Brook '100 percent'

-
 Carrick relishing Frank reunion as Man Utd host Spurs
Carrick relishing Frank reunion as Man Utd host Spurs
-
Farrell keeps the faith in Irish still being at rugby's top table

-
 Meloni, Vance hail 'shared values' amid pre-Olympic protests
Meloni, Vance hail 'shared values' amid pre-Olympic protests
-
Olympic freestyle champion Gremaud says passion for skiing carried her through dark times

-
 US urges new three-way nuclear deal with Russia and China
US urges new three-way nuclear deal with Russia and China
-
Indonesia landslide death toll rises to 74

-
 Hemetsberger a 'happy psychopath' after final downhill training
Hemetsberger a 'happy psychopath' after final downhill training
-
Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 31, wounds over 130

-
 Elton John accuses UK tabloids publisher of 'abhorrent' privacy breaches
Elton John accuses UK tabloids publisher of 'abhorrent' privacy breaches
-
Lindsey Vonn completes first downhill training run at Winter Olympics

-
 Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns
-
Feyi-Waboso out of England's Six Nations opener against Wales

-
 Newcastle manager Howe pleads for Woltemade patience
Newcastle manager Howe pleads for Woltemade patience
-
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost

-
 Portugal heads for presidential vote, fretting over storms and far-right
Portugal heads for presidential vote, fretting over storms and far-right
-
Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 30, wounds over 130: police

-
 Russia says Kyiv behind Moscow shooting of army general
Russia says Kyiv behind Moscow shooting of army general
-
Greenland villagers focus on 'normal life' amid stress of US threat

-
 Iran, US hold talks in Oman after Trump military threats
Iran, US hold talks in Oman after Trump military threats
-
Stocks waver as tech worries build

-
 Dupont, Jalibert click to give France extra spark in Six Nations bid
Dupont, Jalibert click to give France extra spark in Six Nations bid
-
'Excited' Scots out to prove they deserve T20 World Cup call-up

-
 EU tells TikTok to change 'addictive' design
EU tells TikTok to change 'addictive' design
-
India captain admits 'there will be nerves' at home T20 World Cup

-
 Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift
-
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe


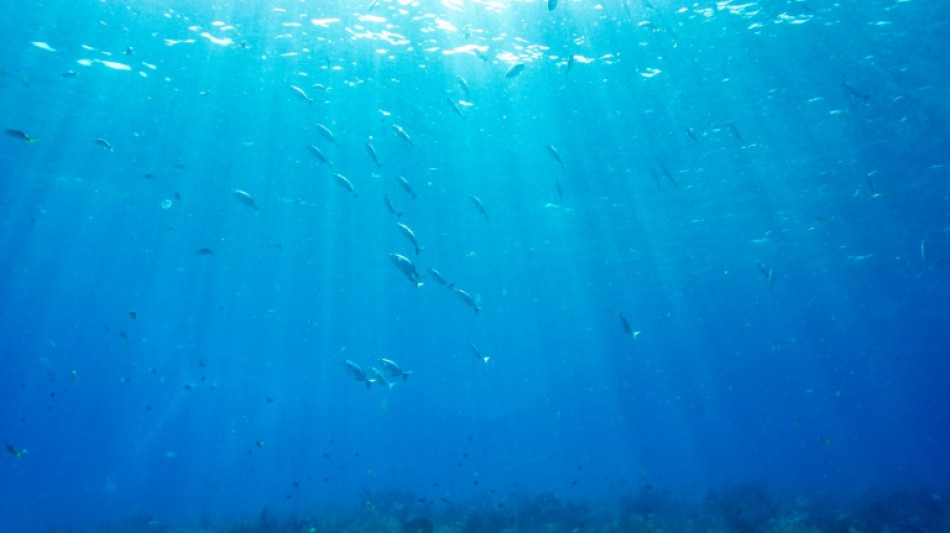
Adagio in sea: Coral larvae 'settle near sounds of healthy reefs'
Audio recordings of healthy reefs -- an underwater chorus of fish songs and crackles from snapping shrimp -- may help efforts to restore coral ecosystems harmed by climate and human impacts, scientists said Wednesday.
With the future of the world's biodiversity-rich coral reefs threatened by climate change, some experts are looking for rehabilitation strategies to go alongside broader efforts to slash planet-heating pollution.
Researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution say one such method to help reefs rebuild could be sound, after they broadcast audio from a healthy reef to entice coral larvae to settle on the seabed at a degraded reef.
Coral larvae use a range of signals from reefs, including chemical cues, as they swim through the open water in their first stage of life looking for a permanent home, said Nadege Aoki, lead author of the study published in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
"Now we have also demonstrated that the local sound environment is very important for these corals, and that playing reef sounds can potentially be a vital tool in the effort to restore coral reefs," she told AFP.
Researchers had been listening to coral reefs in the US Virgin Islands for over a decade, gaining insights into the distinct sounds that separate lively habitats from those that have been damaged by bleaching, disease or direct human impacts.
"A healthy coral reef will typically feature many low-frequency sounds of croaks, purrs, and grunts produced by fishes against a near-constant background of crackles and pops produced by snapping shrimp," said Aoki. A degraded reef, with fewer species, "will be much quieter".
- Under threat -
The team collected specimens from a hardy species known as mustard hill coral -- named for its lumpy shape and yellow hue.
They then distributed them in cups at three reefs in the US Virgin Islands -- one healthy and two more degraded, with patchy coral growth and fewer fish.
Researchers then set up underwater speakers to broadcast their back catalogue of healthy reef sounds at one of the degraded reefs.
They found that the coral larvae at this location settled at rates 1.7 times higher on average -- and up to seven times more -- than the other two reefs, where no sound was played.
There was still much more to learn about how corals respond to sound, Aoki said, including whether different species behave in the same ways and how they are able to "hear".
But she added the finding suggests audio could become part of efforts to rebuild damaged reefs, although this would need to be monitored and protected, since settlement is just one step in a coral's life.
"At the rate that coral reefs are disappearing, human intervention will be absolutely essential to preserving reefs in anything close to their current states," she said.
Coral reefs support about a quarter of all marine life, as well as the millions of people who rely on them for food and income.
But human-driven climate change is spurring mass coral bleaching as the oceans heat and scientists warn that up to 90 percent of reefs could be lost if warming reaches 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
O.Bulka--BTB



