
-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman

-
 US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
 Arteta apologises to Rosenior after disrespect row
Arteta apologises to Rosenior after disrespect row
-
Terror at Friday prayers: witness describes 'extremely powerful' blast in Islamabad

-
 Winter Olympics men's downhill: Three things to watch
Winter Olympics men's downhill: Three things to watch
-
Ice dancers Chock and Bates shine as US lead Japan in team event

-
 Stellantis takes massive hit on 'overestimation' of EV demand
Stellantis takes massive hit on 'overestimation' of EV demand
-
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer

-
 Spanish PM urges caution as fresh rain heads for flood zone
Spanish PM urges caution as fresh rain heads for flood zone
-
Iran says to hold more talks with US despite Trump military threats

-
 Russia accuses Kyiv of gun attack on army general in Moscow
Russia accuses Kyiv of gun attack on army general in Moscow
-
Cambodia reveals damage to UNESCO-listed temple after Thailand clashes

-
 Norway crown princess 'deeply regrets' Epstein friendship
Norway crown princess 'deeply regrets' Epstein friendship
-
Italy set for Winter Olympics opening ceremony as Vonn passes test

-
 England's Jacks says players back under-fire skipper Brook '100 percent'
England's Jacks says players back under-fire skipper Brook '100 percent'
-
Carrick relishing Frank reunion as Man Utd host Spurs

-
 Farrell keeps the faith in Irish still being at rugby's top table
Farrell keeps the faith in Irish still being at rugby's top table
-
Meloni, Vance hail 'shared values' amid pre-Olympic protests

-
 Olympic freestyle champion Gremaud says passion for skiing carried her through dark times
Olympic freestyle champion Gremaud says passion for skiing carried her through dark times
-
US urges new three-way nuclear deal with Russia and China

-
 Indonesia landslide death toll rises to 74
Indonesia landslide death toll rises to 74
-
Hemetsberger a 'happy psychopath' after final downhill training

-
 Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 31, wounds over 130
Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 31, wounds over 130
-
Elton John accuses UK tabloids publisher of 'abhorrent' privacy breaches

-
 Lindsey Vonn completes first downhill training run at Winter Olympics
Lindsey Vonn completes first downhill training run at Winter Olympics
-
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns

-
 Feyi-Waboso out of England's Six Nations opener against Wales
Feyi-Waboso out of England's Six Nations opener against Wales
-
Newcastle manager Howe pleads for Woltemade patience

-
 German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
-
Portugal heads for presidential vote, fretting over storms and far-right

-
 Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 30, wounds over 130: police
Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 30, wounds over 130: police
-
Russia says Kyiv behind Moscow shooting of army general

-
 Greenland villagers focus on 'normal life' amid stress of US threat
Greenland villagers focus on 'normal life' amid stress of US threat
-
Iran, US hold talks in Oman after Trump military threats

-
 Stocks waver as tech worries build
Stocks waver as tech worries build
-
Dupont, Jalibert click to give France extra spark in Six Nations bid

-
 'Excited' Scots out to prove they deserve T20 World Cup call-up
'Excited' Scots out to prove they deserve T20 World Cup call-up
-
EU tells TikTok to change 'addictive' design

-
 India captain admits 'there will be nerves' at home T20 World Cup
India captain admits 'there will be nerves' at home T20 World Cup
-
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift

-
 'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
-
Iran, US hold talks in Oman

-
 Iran, US hold talks in Oman after deadly protest crackdown
Iran, US hold talks in Oman after deadly protest crackdown
-
In Finland's forests, soldiers re-learn how to lay anti-personnel mines

-
 Israeli president visits Australia after Bondi Beach attack
Israeli president visits Australia after Bondi Beach attack
-
In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school

-
 Lakers rally to beat Sixers despite Doncic injury
Lakers rally to beat Sixers despite Doncic injury
-
Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters


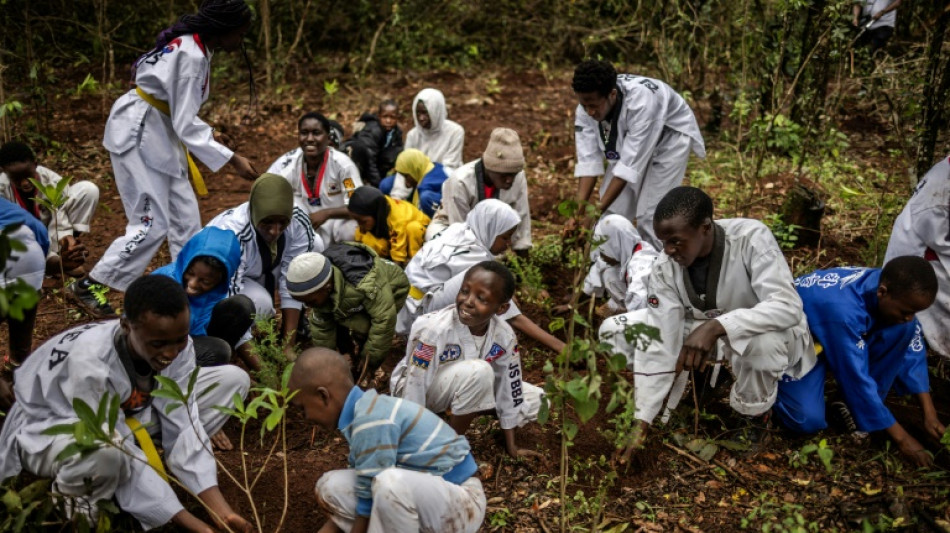
Planting trees in wrong places heats the planet: study
Planting trees in the wrong places can actually contribute to global warming, scientists said on Tuesday, but a new map identifies the best locations to regrow forests and cool the planet.
Trees soak up carbon dioxide and restoring areas of degraded woodlands or planting saplings to boost forest cover is one tool in the fight against climate change.
But in some cases, more trees means less sunlight is reflected back from the earth's surface and more heat is absorbed by the planet, according to a study in the journal Nature Communications.
"There are some places where putting trees back leads to net climate negative outcomes," Susan Cook-Patton, one of the study's co-authors, told AFP.
Scientists had already understood that restoring tree cover led to changes in albedo -- the amount of solar radiation bounced back off the planet's surface -- but didn't have the tools to account for it, she said.
Using new maps, researchers were able to consider, for the first time, the cooling effect from trees and the warming caused by decreased albedo.
They found that projects that didn't factor albedo into the equation overestimated the climate benefit of additional trees by between 20 to 80 percent.
But the maps also provide the tools to help policymakers identify where best to funnel scarce resources for maximum climate impact, said Cook-Patton, senior forest restoration scientist at The Nature Conservancy.
"There's also lots of places still where restoring tree cover is a great idea for climate change. We're just trying to help people find those spots," she said.
- Return on investment -
Albedo is highest in the frozen areas of the world, and mirror-like clean snow and ice with high levels of albedo reflect up to 90 percent of the sun's energy.
It is one of Earth's major cooling agents, along with lands and oceans that absorb excess heat and planet-warming greenhouse gas emissions.
Many countries have promised to plant billions of trees as a bulwark against global warming but not all efforts deliver for the planet equally, this study showed.
Moist, tropical environments like the Amazon and Congo Basin boasted high carbon storage and low changes in albedo, making them ideal locations for restoring forest cover.
The opposite was true in temperate grasslands and savanna, Cook-Patton said.
Even projects in the best locations were probably delivering 20 percent less cooling than estimated when changes to albedo were taken into account, she said.
But she stressed that restoring forests delivered undeniable benefits for people and the planet, such as supporting ecosystems and providing clean air and water, among many.
"We really don't want our work to be a critique of the movement writ large," she said.
"(But) we can't put trees everywhere. We don't have enough money or time or resources or people or seedlings.
"And so it's really about making the most of limited investments and getting the greatest climate return per hectare of investment," she added.
B.Shevchenko--BTB




