
-
 European stocks rise as oil tumbles, while tech worries weigh on New York
European stocks rise as oil tumbles, while tech worries weigh on New York
-
England captain Itoje on bench for Six Nations opener against Wales

-
 Rahm says golfers should be 'free' to play where they want after LIV defections
Rahm says golfers should be 'free' to play where they want after LIV defections
-
More baby milk recalls in France after new toxin rules

-
 Rosenior will not rush Estevao return from Brazil
Rosenior will not rush Estevao return from Brazil
-
Mercedes ready to win F1 world title, says Russell

-
 Germany hit by nationwide public transport strike
Germany hit by nationwide public transport strike
-
Barca coach Flick 'not happy' with Raphinha thigh strain

-
 WHO chief says turmoil creates chance for reset
WHO chief says turmoil creates chance for reset
-
European stocks rise as gold, oil prices tumble

-
 Rink issues resolved, NHL stars chase Olympic gold at Milan
Rink issues resolved, NHL stars chase Olympic gold at Milan
-
S. Korea celebrates breakthrough K-pop Grammy win for 'Golden'

-
 Rodri rages that officials 'don't want' Man City to win
Rodri rages that officials 'don't want' Man City to win
-
Gaza's Rafah crossing makes limited reopening after two-year war

-
 African players in Europe: Ouattara dents Villa title hopes
African players in Europe: Ouattara dents Villa title hopes
-
Liverpool beat Chelsea to Rennes defender Jacquet - reports

-
 S. Korea celebrates breakthrough Grammy win for K-pop's 'Golden'
S. Korea celebrates breakthrough Grammy win for K-pop's 'Golden'
-
Trump says US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba

-
 Trump threatens legal action against Grammy host over Epstein comment
Trump threatens legal action against Grammy host over Epstein comment
-
Olympic Games in northern Italy have German twist

-
 Bad Bunny: the Puerto Rican phenom on top of the music world
Bad Bunny: the Puerto Rican phenom on top of the music world
-
Snapchat blocks 415,000 underage accounts in Australia

-
 At Grammys, 'ICE out' message loud and clear
At Grammys, 'ICE out' message loud and clear
-
Dalai Lama's 'gratitude' at first Grammy win

-
 Bad Bunny makes Grammys history with Album of the Year win
Bad Bunny makes Grammys history with Album of the Year win
-
Stocks, oil, precious metals plunge on volatile start to the week

-
 Steven Spielberg earns coveted EGOT status with Grammy win
Steven Spielberg earns coveted EGOT status with Grammy win
-
Knicks boost win streak to six by beating LeBron's Lakers

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga triumph at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga triumph at Grammys
-
Japan says rare earth found in sediment retrieved on deep-sea mission

-
 San Siro prepares for last dance with Winter Olympics' opening ceremony
San Siro prepares for last dance with Winter Olympics' opening ceremony
-
France great Benazzi relishing 'genius' Dupont's Six Nations return

-
 Grammy red carpet: black and white, barely there and no ICE
Grammy red carpet: black and white, barely there and no ICE
-
Oil tumbles on Iran hopes, precious metals hit by stronger dollar

-
 South Korea football bosses in talks to avert Women's Asian Cup boycott
South Korea football bosses in talks to avert Women's Asian Cup boycott
-
Level playing field? Tech at forefront of US immigration fight

-
 British singer Olivia Dean wins Best New Artist Grammy
British singer Olivia Dean wins Best New Artist Grammy
-
Hatred of losing drives relentless Alcaraz to tennis history

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga win early at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga win early at Grammys
-
Surging euro presents new headache for ECB

-
 Djokovic hints at retirement as time seeps away on history bid
Djokovic hints at retirement as time seeps away on history bid
-
US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba: Trump

-
 UK ex-ambassador quits Labour over new reports of Epstein links
UK ex-ambassador quits Labour over new reports of Epstein links
-
Trump says closing Kennedy Center arts complex for two years

-
 Formerra and Evonik Expand Distribution Partnership for Healthcare Grades
Formerra and Evonik Expand Distribution Partnership for Healthcare Grades
-
Hans Vestberg, Former Verizon Chairman and CEO, Joins Digipower X As Senior Advisor
-
 Reigning world champs Tinch, Hocker among Millrose winners
Reigning world champs Tinch, Hocker among Millrose winners
-
Venezuelan activist ends '1,675 days' of suffering in prison

-
 Real Madrid scrape win over Rayo, Athletic claim derby draw
Real Madrid scrape win over Rayo, Athletic claim derby draw
-
PSG beat Strasbourg after Hakimi red to retake top spot in Ligue 1


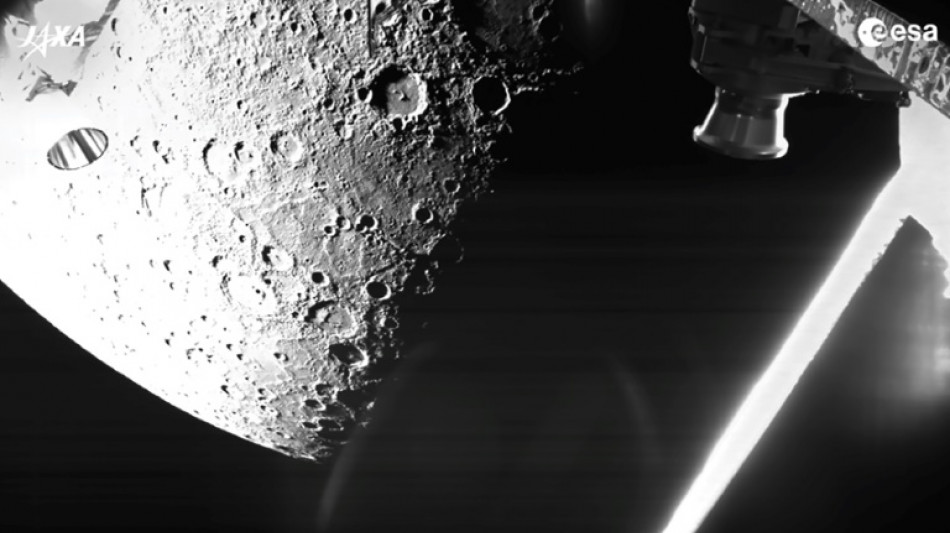
Spacecraft flies closer to Mercury than planned after thruster glitch
A spacecraft carrying European and Japanese probes passed closer to Mercury than originally planned overnight after thruster problems delayed the mission to study the little-known, Sun-scorched planet.
The BepiColombo mission launched in 2018 on a winding path that had been intended to enter the orbit of the planet closest to the Sun in December 2025.
But in April, a glitch with the spacecraft's thrusters sapped some of its power supply, forcing teams on the ground to change its trajectory and delaying its arrival until November 2026.
The new path meant the spacecraft needed to fly 35 kilometres (22 miles) closer to the planet than initially planned -- passing just 165 kilometres above the surface -- during its latest flyby.
The European Space Agency's operations team confirmed that "all went well" with the flyby overnight, the mission's account on X said on Thursday.
It also posted a new image taken by the probe of the planet, whose pockmarked surface resembles the Moon.
It was the fourth of six planned flybys of Mercury on the mission's nine-billion-kilometre journey before it can finally settle into the planet's orbit.
Most of the time Mercury is closer to Earth than Mars -- but the red planet can be reached by missions from Earth in just seven months.
Mercury is "the most difficult" planet for probes to reach, explained Paris Observatory astronomer Alain Doressoundiram.
The planet's relatively tiny mass -- it is only slightly bigger than the Moon -- means its gravitational pull is extremely weak compared to the Sun, making it tricky for satellites to stay in its orbit.
"It takes much more energy to brake and stop at Mercury than to go to Mars," Doressoundiram told AFP.
This is where delicate manoeuvres called gravitational assists come in. These slingshots around celestial bodies allow spacecraft to speed up, slow down, or change trajectory.
The glitch with the electric thrusters means the spacecraft is now operating with only 90 percent of its planned power supply.
After months spent investigating the problem, the thrusters will "remain operating below the minimum thrust required for an insertion into orbit around Mercury in December 2025," mission manager Santa Martinez said in a statement earlier this week.
The new slower path means BepiColombo is now planned to enter orbit in November 2026.
- Space 'oddities' -
Mercury is by far the least studied of the four rocky, innermost planets in our solar system, which also include Venus, Earth and Mars.
NASA's Mariner 10 was the first probe to capture a close picture of its lunar-looking surface in 1974.
No spacecraft had orbited the planet until the MESSENGER probe arrived in 2011.
The NASA mission confirmed "some rather bizarre things," said Doressoundiram, a specialist on the surfaces of planets.
One of these "oddities" is that Mercury is the only rocky planet other than Earth to have a magnetic field, Doressoundiram said. Exactly how it has such a magnetic field so close to the Sun is not fully understood.
Another "oddity" is that Mercury's iron core composes 60 percent of its mass -- compared to only a third for Earth.
Mercury's surface is also marked by "hollows," which could suggest relatively recent geologic activity.
Also unclear is the composition of minerals on covering the planet's surface, which is blasted with intense radiation from the Sun.
These are just some of the mysteries that the BepiColombo mission hopes to shed light on when it finally orbits Mercury for at least a year and a half.
The spacecraft carries two separate satellites, one from the ESA and another from Japan's JAXA space agency, which have a total of 16 scientific instruments.
P.Anderson--BTB



