
-
 Germany hit by nationwide public transport strike
Germany hit by nationwide public transport strike
-
Barca coach Flick 'not happy' with Raphinha thigh strain

-
 WHO chief says turmoil creates chance for reset
WHO chief says turmoil creates chance for reset
-
European stocks rise as gold, oil prices tumble

-
 Rink issues resolved, NHL stars chase Olympic gold at Milan
Rink issues resolved, NHL stars chase Olympic gold at Milan
-
S. Korea celebrates breakthrough K-pop Grammy win for 'Golden'

-
 Rodri rages that officials 'don't want' Man City to win
Rodri rages that officials 'don't want' Man City to win
-
Gaza's Rafah crossing makes limited reopening after two-year war

-
 African players in Europe: Ouattara dents Villa title hopes
African players in Europe: Ouattara dents Villa title hopes
-
Liverpool beat Chelsea to Rennes defender Jacquet - reports

-
 S. Korea celebrates breakthrough Grammy win for K-pop's 'Golden'
S. Korea celebrates breakthrough Grammy win for K-pop's 'Golden'
-
Trump says US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba

-
 Trump threatens legal action against Grammy host over Epstein comment
Trump threatens legal action against Grammy host over Epstein comment
-
Olympic Games in northern Italy have German twist

-
 Bad Bunny: the Puerto Rican phenom on top of the music world
Bad Bunny: the Puerto Rican phenom on top of the music world
-
Snapchat blocks 415,000 underage accounts in Australia

-
 At Grammys, 'ICE out' message loud and clear
At Grammys, 'ICE out' message loud and clear
-
Dalai Lama's 'gratitude' at first Grammy win

-
 Bad Bunny makes Grammys history with Album of the Year win
Bad Bunny makes Grammys history with Album of the Year win
-
Stocks, oil, precious metals plunge on volatile start to the week

-
 Steven Spielberg earns coveted EGOT status with Grammy win
Steven Spielberg earns coveted EGOT status with Grammy win
-
Knicks boost win streak to six by beating LeBron's Lakers

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga triumph at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga triumph at Grammys
-
Japan says rare earth found in sediment retrieved on deep-sea mission

-
 San Siro prepares for last dance with Winter Olympics' opening ceremony
San Siro prepares for last dance with Winter Olympics' opening ceremony
-
France great Benazzi relishing 'genius' Dupont's Six Nations return

-
 Grammy red carpet: black and white, barely there and no ICE
Grammy red carpet: black and white, barely there and no ICE
-
Oil tumbles on Iran hopes, precious metals hit by stronger dollar

-
 South Korea football bosses in talks to avert Women's Asian Cup boycott
South Korea football bosses in talks to avert Women's Asian Cup boycott
-
Level playing field? Tech at forefront of US immigration fight

-
 British singer Olivia Dean wins Best New Artist Grammy
British singer Olivia Dean wins Best New Artist Grammy
-
Hatred of losing drives relentless Alcaraz to tennis history

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga win early at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga win early at Grammys
-
Surging euro presents new headache for ECB

-
 Djokovic hints at retirement as time seeps away on history bid
Djokovic hints at retirement as time seeps away on history bid
-
US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba: Trump

-
 UK ex-ambassador quits Labour over new reports of Epstein links
UK ex-ambassador quits Labour over new reports of Epstein links
-
Trump says closing Kennedy Center arts complex for two years

-
 Hans Vestberg, Former Verizon Chairman and CEO, Joins Digipower X As Senior Advisor
Hans Vestberg, Former Verizon Chairman and CEO, Joins Digipower X As Senior Advisor
-
Reigning world champs Tinch, Hocker among Millrose winners

-
 Venezuelan activist ends '1,675 days' of suffering in prison
Venezuelan activist ends '1,675 days' of suffering in prison
-
Real Madrid scrape win over Rayo, Athletic claim derby draw

-
 PSG beat Strasbourg after Hakimi red to retake top spot in Ligue 1
PSG beat Strasbourg after Hakimi red to retake top spot in Ligue 1
-
NFL Cardinals hire Rams' assistant LaFleur as head coach

-
 Arsenal scoop $2m prize for winning FIFA Women's Champions Cup
Arsenal scoop $2m prize for winning FIFA Women's Champions Cup
-
Atletico agree deal to sign Lookman from Atalanta

-
 Real Madrid's Bellingham set for month out with hamstring injury
Real Madrid's Bellingham set for month out with hamstring injury
-
Man City won't surrender in title race: Guardiola

-
 Korda captures weather-shortened LPGA season opener
Korda captures weather-shortened LPGA season opener
-
Czechs rally to back president locking horns with government


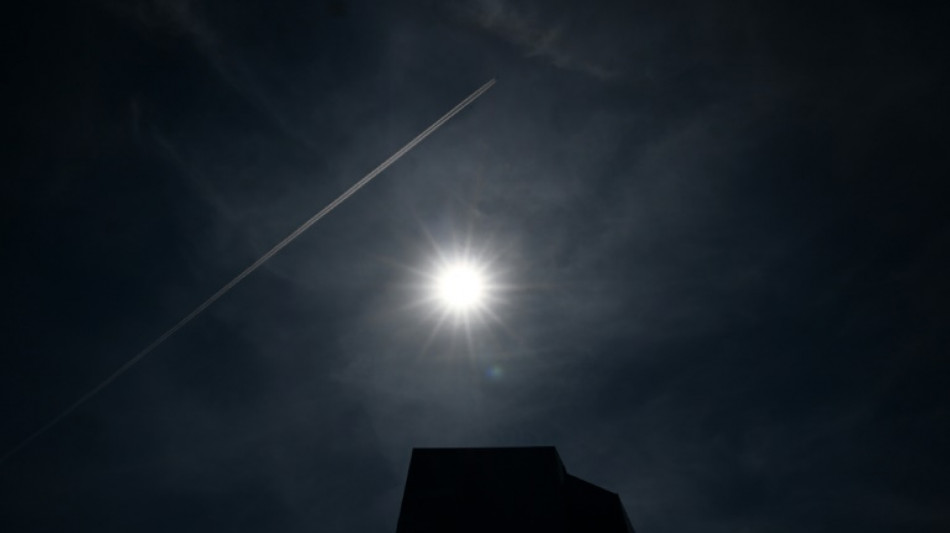
Plane contrails: white fluffy contributors to global warming
The white, feathery lines behind airplanes that look like bits of harmless cloud are anything but, warn experts, who say they could have a greater environmental impact than the aviation sector's CO2 emissions.
The condensation trails -- contrails, for short -- are being increasingly studied as scientists work with the industry to find technological solutions to the problem.
Classified as non-CO2 emissions from aircraft, in September they were the subject of a symposium in Montreal organized by the International Civil Aviation Organization, a UN agency.
- What are contrails? -
Contrails are clouds that form at high altitudes in cold, humid areas called ice supersaturated regions (ISSRs).
When jet fuel is burned by engines, water vapor condenses on to soot particles to form ice crystals.
Enough ice crystals, and they begin to form cirrus clouds -- high-altitude, wispy white filaments that, when created this way, trail out behind planes as they cross the sky.
These trails trap some of the heat that rises from the Earth at night, preventing it from radiating back out of the atmosphere -- thus acting as a greenhouse gas, causing warming, explains Donald Wuebbles, a professor at the University of Illinois.
Contrails that stay in the sky for a few minutes are not very worrisome, he says.
"But if they form at night, they'll maybe last a little longer, and at night they can cause a warming effect," he adds.
- What is the impact? -
Non-CO2 emissions could account for up to two-thirds of aviation's impact on global warming, which "gives you an idea of how important they are to consider," Wuebbles said.
And contrails could form up to 57 percent of that impact -- far more than the C02 emissions from burning fuel, according to a 2021 study.
However, such emissions are short-lived compared to carbon dioxide and their impact on global warming could be quickly eroded if solutions were found to avoid them, experts say.
- So what can be done? -
Not all flights create contrails -- it can depend on weather conditions and the aircraft's trajectory.
For example, at Air France, just four percent of flights are responsible for some 80 percent of the airline's contrail impact on global warming, notes Irene Boyer-Souchet, who is leading up the company's efforts to mitigate the damage.
The long-term strategy is to modify the trajectory of a fraction of flights.
Air France pilots made more than 3,000 observations over 18 months with the aim of helping Meteo-France improve its forecasts for at-risk areas so that pilots could eventually avoid them.
"The main risk is that by thinking you're avoiding an area, you could end up flying there because it's slightly off the weather forecast," Boyer-Souchet points out, illustrating the importance of fine-tuning the research.
Pilots from American Airlines conducted 70 test flights above or below at-risk areas, guided by satellite images, weather data, software models and AI prediction tools.
A 54-percent reduction in contrails was observed, along with a two-percent increase in fuel consumption.
Accelerating the deployment of a global contrail avoidance system could reduce aviation's impact on the climate by 40 percent, according to a Cambridge University report published in September.
The more flights in the air, however, the more complicated the implementation of such a system would be, notes Boyer-Souchet, who hopes that it will be a reality by 2030.
K.Brown--BTB



