-
 Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
-
Gaza civil defence says Israeli strikes kill 28

-
 Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
-
Melbourne champion Rybakina never doubted return to Wimbledon form

-
 Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
-
Long truck lines at Colombia-Ecuador border as tariffs loom

-
 Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
-
Separatist attacks in Pakistan kill 21, dozens of militants dead

-
 'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
-
Arbeloa backs five Real Madrid stars he 'always' wants playing

-
 Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
-
Britain, Japan agree to deepen defence and security cooperation

-
 Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
-
France tightens infant formula rules after toxin scare

-
 Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's Moscow-born Melbourne champion

-
 Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
-
Pakistan attacks kill 15, dozens of militants dead: official

-
 Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
-
Epstein survivors say abusers 'remain hidden' after latest files release

-
 'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
-
Wollaston goes back-to-back in the Cadel Evans road race

-
 Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
-
Ship ahoy! Prague's homeless find safe haven on river boat

-
 Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
-
Carlos Alcaraz: rare tennis talent with shades of Federer

-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January

-
 Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
-
Bad Bunny set for historic one-two punch at Grammys, Super Bowl

-
 Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
-
Venezuelan interim president proposes mass amnesty law

-
 Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
-
Online foes Trump, Petro set for White House face-to-face

-
 Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
-
US Senate passes deal expected to shorten shutdown

-
 'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
-
Thousands rally in Minneapolis as immigration anger boils

-
 US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
-
Lens win to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1 from PSG

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
-
Ko, Woad share lead at LPGA season opener


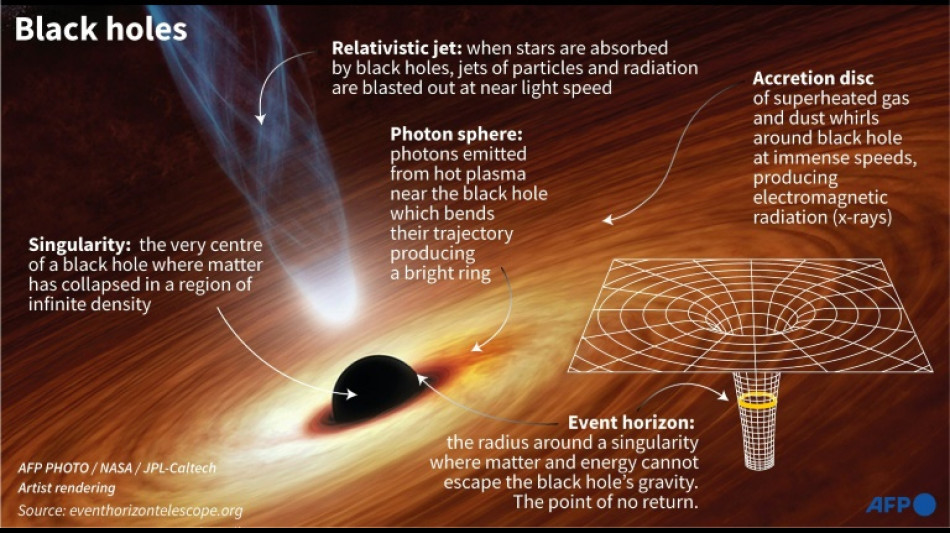
Astronomers reveal first image of black hole at Milky Way's centre
An international team of astronomers on Thursday unveiled the first image of a supermassive black hole at the centre of our own Milky Way galaxy -- a cosmic body known as Sagittarius A*.
The image -- produced by a global team of scientists known as the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration -- is the first, direct visual confirmation of the presence of this invisible object, and comes three years after the very first image of a black hole from a distant galaxy.
Black holes are regions of space where the pull of gravity is so intense that nothing can escape, including light.
The image thus depicts not the black hole itself, because it is completely dark, but the glowing gas that encircles the phenomenon -- which is four million times more massive than our Sun -- in a bright ring of bending light.
"These unprecedented observations have greatly improved our understanding of what happens at the very centre of our galaxy," said EHT project scientist Geoffrey Bower, of Taiwan's Academia Sinica.
Bower also said in a statement provided by the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) that the observations had offered "new insights on how these giant black holes interact with their surroundings".
The results are published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
- Virtual telescope -
Sagittarius A* -- abbreviated to Sgr A*, which is pronounced "sadge-ay-star" -- owes its name to its detection in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius.
Its existence has been assumed since 1974, with the detection of an unusual radio source at the centre of the galaxy.
In the 1990s, astronomers mapped the orbits of the brightest stars near the centre of the Milky Way, confirming the presence of a supermassive compact object there -- work that led to the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Though the presence of a black hole was thought to be the only plausible explanation, the new image provides the first direct visual proof.
Because it is 27,000 light years from Earth, it appears the same size in the sky as a donut on the Moon.
Capturing images of such a faraway object required linking eight giant radio observatories across the planet to form a single "Earth-sized" virtual telescope called the EHT.
These included the Institute for Millimetre Radio Astronomy (IRAM) 30-meter telescope in Spain, the most sensitive single antenna in the EHT network.
The EHT gazed at Sgr A* across multiple nights for many hours in a row -- a similar idea to long-exposure photography and the same process used to produce the first image of a black hole, released in 2019.
That black hole is called M87* because it is in the Messier 87 galaxy.
- Moving target -
The two black holes bear striking similarities, despite the fact that Sgr A* is 2,000 times smaller than M87*.
"Close to the edge of these black holes, they look amazingly similar," said Sera Markoff, co-chair of the EHT Science Council, and a professor at the University of Amsterdam.
Both behaved as predicted by Einstein's 1915 theory of General Relativity, which holds that the force of gravity results from the curvature of space and time, and cosmic objects change this geometry.
Despite the fact Sgr A* is much closer to us, imaging it presented unique challenges.
Gas in the vicinity of both black holes moves at the same speed, close to the speed of light. But while it took days and weeks to orbit the larger M87*, it completed rounds of Sgr A* in just minutes.
The researchers had to develop complex new tools to account for the moving targets.
The resulting image -- the work of more than 300 researchers across 80 countries over a period of five years -- is an average of multiple images that revealed the invisible monster lurking at the centre of the galaxy.
Scientists are now eager to compare the two black holes to test theories about how gasses behave around them -- a poorly understood phenomenon thought to play a role in the formation of new stars and galaxies.
Probing black holes -- in particular their infinitely small and dense centers known as singularities, where Einstein's equations break down -- could help physicists deepen their understanding of gravity and develop a more advanced theory.
H.Seidel--BTB




