-
 La Rochelle suffer defeat after shock Atonio retirement
La Rochelle suffer defeat after shock Atonio retirement
-
'It wasn't working': Canada province ends drug decriminalization

-
 Kishan, Arshdeep star as India down New Zealand in T20 finale
Kishan, Arshdeep star as India down New Zealand in T20 finale
-
Moreno bags brace but Villarreal held at Osasuna

-
 Kramaric keeps in-form Hoffenheim rolling in Bundesliga
Kramaric keeps in-form Hoffenheim rolling in Bundesliga
-
'Skimo': Adrenalin-packed sprint to make Olympic debut

-
 Venezuela's 'Helicoide' prison synonymous with torture of dissenters
Venezuela's 'Helicoide' prison synonymous with torture of dissenters
-
Arsenal thrash Leeds to stretch Premier League advantage

-
 Russia's Valieva returns to ice after doping ban
Russia's Valieva returns to ice after doping ban
-
Snow storm barrels into southern US as blast of icy weather widens

-
 Ukraine sees mass power outages from 'technical malfunction'
Ukraine sees mass power outages from 'technical malfunction'
-
Gaza civil defence says Israeli strikes kill 32

-
 Kirsty Coventry set to give clues to her Olympic vision in Milan
Kirsty Coventry set to give clues to her Olympic vision in Milan
-
I'm no angel, Italy's PM says amid church fresco row

-
 Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
-
Gaza civil defence says Israeli strikes kill 28

-
 Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
-
Melbourne champion Rybakina never doubted return to Wimbledon form

-
 Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
-
Long truck lines at Colombia-Ecuador border as tariffs loom

-
 Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
-
Separatist attacks in Pakistan kill 21, dozens of militants dead

-
 'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
-
Arbeloa backs five Real Madrid stars he 'always' wants playing

-
 Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
-
Britain, Japan agree to deepen defence and security cooperation

-
 Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
-
France tightens infant formula rules after toxin scare

-
 Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's Moscow-born Melbourne champion

-
 Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
-
Pakistan attacks kill 15, dozens of militants dead: official

-
 Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
-
Epstein survivors say abusers 'remain hidden' after latest files release

-
 'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
-
Wollaston goes back-to-back in the Cadel Evans road race

-
 Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
-
Ship ahoy! Prague's homeless find safe haven on river boat

-
 Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
-
Carlos Alcaraz: rare tennis talent with shades of Federer

-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January


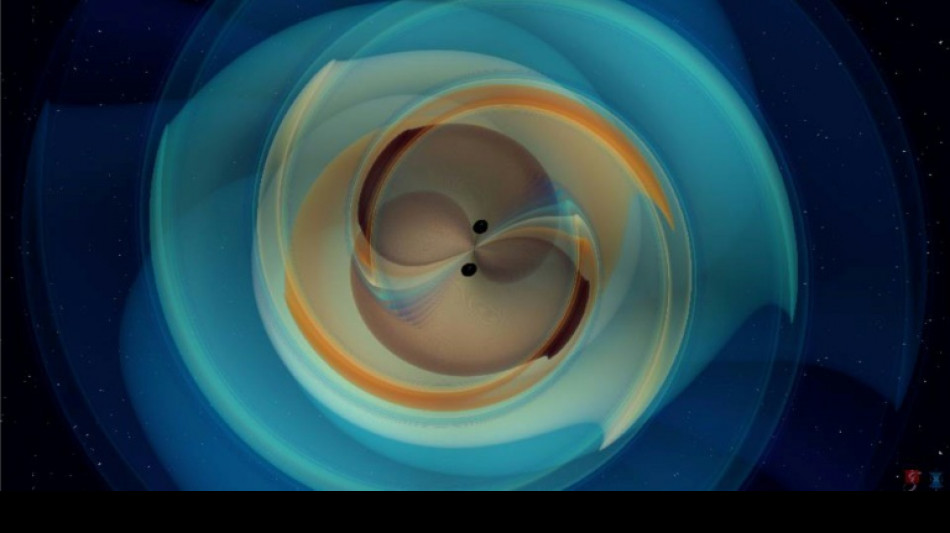
Gravitational waves from black hole smash confirm Hawking theory
Ripples in spacetime sent hurtling through the universe when two black holes smash into each other -- a phenomenon predicted by Albert Einstein -- have confirmed a theory proposed by fellow physicist Stephen Hawking over 50 years ago, scientists announced Wednesday.
These ripples, which are called gravitational waves, were detected for the first time in 2015 by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in the United States.
In his 1916 theory of general relativity, Einstein predicted that the cataclysmic merger of two black holes would produce gravitational waves that would ripple across the universe and eventually arrive at Earth.
On January 14 this year, LIGO detected another of these signals from the distant universe.
That is no longer such a surprise.
Scientists in the LVK collaboration -- a vast network of scientists whose facilities includes gravitational wave detectors in Italy and Japan -- now record a new black hole merger roughly once every three days.
However January was "the loudest gravitational wave event we have detected to date," LIGO member Geraint Pratten of the University of Birmingham, England, said in a statement.
- From a whisper to a shout -
"It was like a whisper becoming a shout," added the co-author of a new study in the Physical Review Letters.
The latest event bore striking similarities to the first one detected a decade ago.
Both involved collisions of black holes with masses of between 30-40 times that of our Sun. And both smash-ups occurred around 1.3 billion light years away.
But thanks to technological improvements over the years, scientists are now able to greatly reduce the background noise, giving them far clearer data.
This allowed the researchers to confirm a theory by another great physicist.
In 1971, Stephen Hawking predicted that a black hole's event horizon -- the area from which nothing including light can escape -- cannot shrink.
This means that when two black holes merge, the new monster they create must have the same or larger surface area than the pair started out with.
Scientists analysing January's merger, called GW250114, were able to show that Hawking was right.
- Ringing like a struck bell -
The black holes collectively started out at 240,000 square kilometres wide, which is roughly the size of the United Kingdom.
But after the collision, the resulting mega-black hole took up 400,000 square kilometres -- about the size of Sweden.
The California Institute of Technology said that working out the final merged surface area was "the trickiest part of this type of analysis".
"The surface areas of pre-merger black holes can be more readily gleaned as the pair spiral together, roiling space-time and producing gravitational waves," it said in a statement.
But the signal gets muddier once the black holes start combining into a single new monster.
This period is called the "ringdown phase", because the merged black hole rings like a struck bell -- a phenomenon that Einstein also predicted.
The scientists were able to measure different frequencies emanating from this rung bell, allowing them to determine the size of the new post-merger black hole.
- Kerr theory vindicated -
This also enabled them to confirm the event aligned with another theory, made by New Zealand mathematician Roy Kerr in 1963.
Kerr predicted that "two black holes with the same mass and spin are mathematically identically," a feature unique to black holes, Maximiliano Isi of Columbia University said in a statement.
Gregorio Carullo of the University of Birmingham said that "given the clarity of the signal produced by GW250114, for the first time we could pick out two 'tones' from the black hole voices and confirm that they behave according to Kerr's prediction."
Scientists are working to find out more about black hole mergers, with several new gravitational wave detectors planned for the coming years -- including one in India.
M.Ouellet--BTB




