-
 Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
-
Gaza civil defence says Israeli strikes kill 28

-
 Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
-
Melbourne champion Rybakina never doubted return to Wimbledon form

-
 Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
-
Long truck lines at Colombia-Ecuador border as tariffs loom

-
 Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
-
Separatist attacks in Pakistan kill 21, dozens of militants dead

-
 'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
-
Arbeloa backs five Real Madrid stars he 'always' wants playing

-
 Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
-
Britain, Japan agree to deepen defence and security cooperation

-
 Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
-
France tightens infant formula rules after toxin scare

-
 Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's Moscow-born Melbourne champion

-
 Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
-
Pakistan attacks kill 15, dozens of militants dead: official

-
 Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
-
Epstein survivors say abusers 'remain hidden' after latest files release

-
 'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
-
Wollaston goes back-to-back in the Cadel Evans road race

-
 Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
-
Ship ahoy! Prague's homeless find safe haven on river boat

-
 Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
-
Carlos Alcaraz: rare tennis talent with shades of Federer

-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January

-
 Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
-
Bad Bunny set for historic one-two punch at Grammys, Super Bowl

-
 Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
-
Venezuelan interim president proposes mass amnesty law

-
 Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
-
Online foes Trump, Petro set for White House face-to-face

-
 Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
-
US Senate passes deal expected to shorten shutdown

-
 'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
-
Thousands rally in Minneapolis as immigration anger boils

-
 US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
-
Lens win to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1 from PSG

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
-
Ko, Woad share lead at LPGA season opener


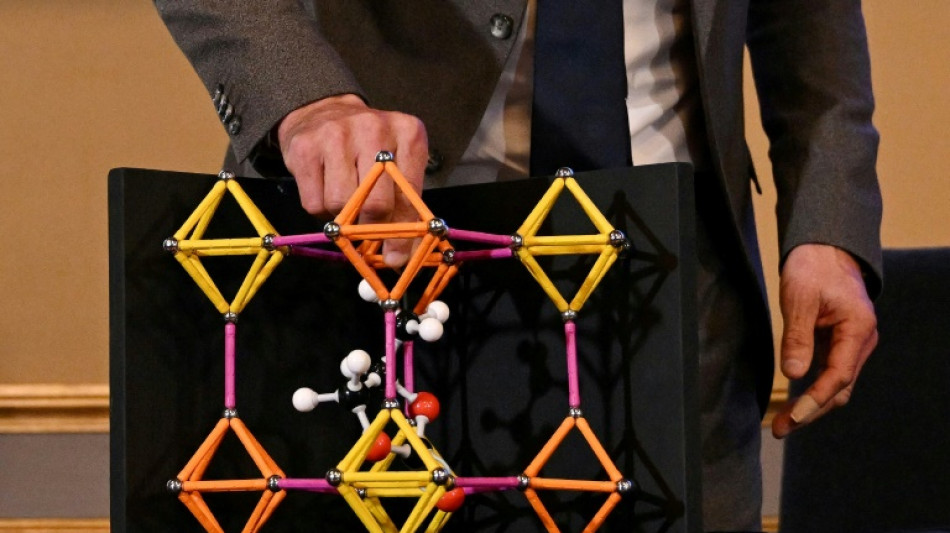
'Solids full of holes': Nobel-winning materials explained
The chemistry Nobel was awarded on Wednesday to three scientists who discovered a revolutionary way of making materials full of tiny holes that can do everything from sucking water out of the desert air to capturing climate-warming carbon dioxide.
The particularly roomy molecular architecture, called metal-organic frameworks, has also allowed scientists to filter "forever chemicals" from water, smuggle drugs into bodies -- and even slow the ripening of fruit.
After Japan's Susumu Kitagawa, UK-born Richard Robson and American-Jordanian Omar Yaghi won their long-anticipated Nobel Prize, here is what you need to know about their discoveries.
- What are metal-organic frameworks? -
Imagine you turn on the hot water for your morning shower, David Fairen-Jimenez, a professor who studies metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) at the University of Cambridge, told AFP.
The mirror in your bathroom fogs up as water molecules collect on its flat surface -- but it can only absorb so much.
Now imagine this mirror was made of a material that was extremely porous -- full of tiny holes -- and these holes were "the size of a water molecule," Fairen-Jimenez said.
This material would be able to hold far more water -- or other gases -- than seems possible.
At the Nobel ceremony, this secret storage ability was compared to Hermione's magical handbag in Harry Potter.
The inside space of a couple of grams of a particular MOF "holds an area as big as a football pitch," the Nobels said in a statement.
Ross Forgan, a professor of materials chemistry at the University of Glasgow, told AFP to think of MOFs as "solids that are full of holes".
They could look essentially like table salt, but "they have a ridiculously high storage capacity inside them because they are hollow -- they can soak up other molecules like a sponge."
- What did the Nobel-winners do? -
In the 1980s, Robson taught his students at Australia's University of Melbourne about molecular structures using wooden balls that played the role of atoms, connected by rods representing chemical bonds.
One day this inspired him to try to link different kinds of molecules together. By 1989, he had drawn out a crystal structure similar to a diamond's -- except that it was full of massive holes.
French researcher David Farrusseng compared the structure of MOFs to the Eiffel Tower. "By interlocking all the iron beams -- horizontal, vertical, and diagonal -- we see cavities appear," he told AFP.
However Robson's holey structures were unstable, and it took years before anyone could figure out what to do with them.
In 1997, Kitagawa finally managed to show that a MOF could absorb and release methane and other gases.
It was Yaghi who coined the term metal-organic frameworks and demonstrated to the world just how much room there was in materials made from them.
- What can they do? -
Because these frameworks can be assembled in different ways -- somewhat like playing with Lego -- companies and labs around the world have been testing out their capabilities.
"This is a field that's generating incredible enthusiasm and is moving extremely fast," Thierry Loiseau of French research centre CNRS told AFP.
More than 100,000 different kinds have already been reported in scientific literature, according to a Cambridge University database.
"Every single month, there are 500 new MOFs," Fairen-Jimenez said.
He and Forgan agreed that likely the greatest impact MOFs will have on the world are in the areas of capturing carbon and delivering drugs.
Though much hyped, efforts to capture carbon dioxide -- the driver of human-caused global warming -- have so far failed to live up to their promise.
Forgan said he was once "a bit sceptical about carbon capture, but now we're finally refining (the MOFs) to the point where they are meeting all the industrial requirements".
Canadian chemical producer BASF says it is the first company to produce hundreds of tons of MOFs a year, for carbon capture efforts.
And Yaghi himself has demonstrated that a MOF material was able to harvest water vapour from the night air in the desert US state of Arizona.
Once the rising Sun heated up the material, his team collected the drinkable water.
L.Janezki--BTB




