
-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
-
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'

-
 'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer

-
 Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
-
Stocks stabilise after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse

-
 Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
-
China calls EU 'discriminatory' over probe into energy giant Goldwind

-
 Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
-
Can Vonn defy ACL rupture to win Olympic medal?

-
 Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
-
German far-right MP detained over alleged Belarus sanctions breach


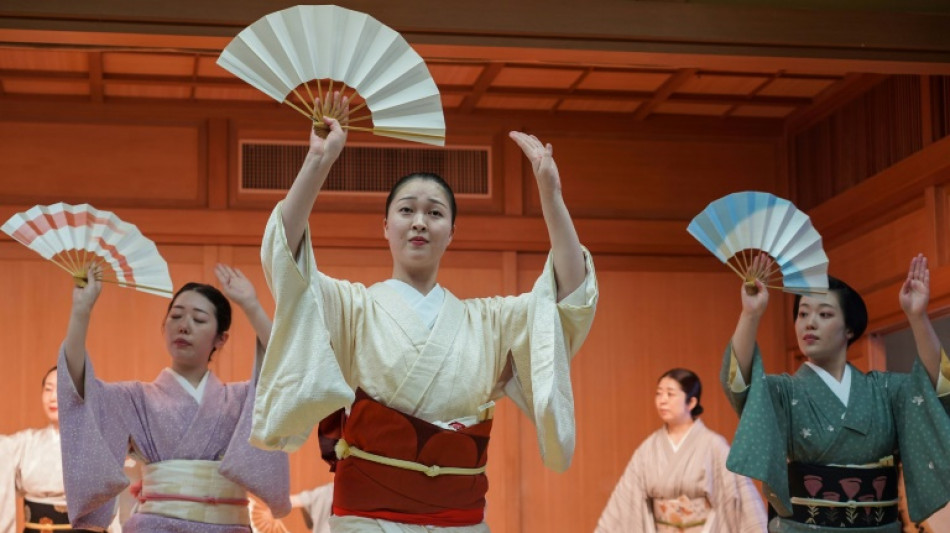
Century-old Tokyo geisha festival revives dying art
The geishas glide with measured steps across a wooden stage, offering a glimpse of a long-misunderstood tradition that is becoming a rare sight in Japan.
Dancing with paper fans and dressed in kimonos, the entertainers were rehearsing without the striking white make-up and sculpted hairstyles they are famous for.
But for seven days from Wednesday the women will perform in full splendour at the 100-year-old Azuma Odori festival at a theatre in the heart of the Japanese capital.
In the popular imagination geishas are often confused with courtesans, but in fact their work -- as trained masters of refined old artforms -- does not involve selling sex.
"Japanese people themselves often don't understand or have the wrong idea about what geishas do," Hisafumi Iwashita, a writer specialised in geisha culture, told AFP.
In Japanese, the word geisha means "person of the arts" — a woman or man trained in traditional Japanese performing arts. But the core role of geishas goes far beyond "just dancing and singing," Iwashita said.
Geishas in different parts of Japan are also known for different skills.
In Kyoto, where they are called geikos, "dance is seen as the most important artform," Iwashita said.
Tokyo geishas meanwhile are known for their singing and talents on the shamisen, which resembles a slim three-stringed guitar.
This year for the first time ever, geishas from 19 Japanese regions are participating in the annual Azuma Odori, as well as those from Tokyo's Shinbashi district who usually perform.
Around 180 geishas will take part overall, taking to the stage in small groups for two shows each day.
Koiku, a Shinbashi geisha, said her job first and foremost involves "welcoming and entertaining visitors at traditional restaurants called ryotei".
Entry to these expensive, exclusive establishments, found in historic geisha districts known as hanamachi, is by invitation only.
- 10 year's training -
Today around 40 geishas work in Shinbashi -- many fewer than in times gone by -- and all of them will appear at the Azuma Odori.
"Not so long ago, there were 100 of us, then 60... and the number keeps going down," Koiku said.
Life as a geisha is tough, with a strict practice schedule even for established performers.
"In general, it takes 10 years to be seen as competent," said Koiku, who was enticed by her love of music and dance.
The geishas' choreography, watched by their instructors and accompanied by live musicians at the rehearsal, includes playful touches such as miming the movements of a fox.
It is not polite to ask a geisha's age, but some taking part in the show have been performing for five or six decades.
Koiku said she is worried that if nothing changes, it will be "too late" for the waning geisha tradition.
Azuma Odori's roots date back to Japan's 1868-1912 Meiji era, when dance began to take a more central role in geisha performances.
Geishas, who would entertain government officials at banquets, played "a key role" in shaping modern Japanese culture, according to the expert Iwashita.
He thinks the main reason for the falling number of geishas in Japan is simply that they have fewer clients.
While geishas once made a living from Japan's wealthy elite, in 1993 then-prime minister Morihiro Hosokawa called for an end to government banquets in ryotei restaurants.
That was a "tough blow for the industry", Iwashita said.
Koiku agrees that the "world has changed" -- including the type of socialising where business deals are sought.
"Nowadays, companies are increasingly organising receptions in their offices or other venues," she said.
Shinbashi Enbujo Theatre, where Azuma Odori will take place, was inaugurated in 1925 with the festival's first edition.
It was rebuilt in 1948 after being destroyed in World War II, and its lavish post-war performances influenced Japanese kabuki theatre before being simplified to audience tastes.
With the future of the geisha profession uncertain, for Iwashita, "the fact that such a theatre still exists, and that it is the 100th anniversary (of Azuma Odori) is nothing short of a miracle".
Y.Bouchard--BTB


