-
 More than 600 British Empire artefacts stolen from museum: police
More than 600 British Empire artefacts stolen from museum: police
-
Ben Sulayem to stand unopposed as FIA election goes ahead

-
 OpenAI, Disney to let fans create AI videos in landmark deal
OpenAI, Disney to let fans create AI videos in landmark deal
-
US trade gap shrinks to narrowest since 2020 after tariff hikes

-
 NATO chief says a joint plan to end Ukraine war would 'test' Putin
NATO chief says a joint plan to end Ukraine war would 'test' Putin
-
Man United say financial results show 'transformation' of club

-
 British cycling great Hoy recovers from 'worst' crash
British cycling great Hoy recovers from 'worst' crash
-
Nobel laureate Machado says US helped her leave Venezuela, vows return

-
 German growth forecasts slashed, Merz under pressure
German growth forecasts slashed, Merz under pressure
-
Emotional Nobel laureate Machado describes reuniting with her children

-
 Thai, Cambodian border evacuees split over Trump mediation
Thai, Cambodian border evacuees split over Trump mediation
-
Bulgarian government resigns after mass protests: PM

-
 Thyssenkrupp pauses steel production at two sites citing Asian pressure
Thyssenkrupp pauses steel production at two sites citing Asian pressure
-
Swiss yodelling joins world cultural heritage list

-
 Stocks diverge as AI fears cloud US rate cut
Stocks diverge as AI fears cloud US rate cut
-
Israel says Hamas 'will be disarmed' after group proposes weapons freeze

-
 ECB proposes simplifying rules for banks
ECB proposes simplifying rules for banks
-
Toll in deadly Indonesia floods near 1,000, frustrations grow

-
 Myanmar junta air strike on hospital kills 31, aid workers say
Myanmar junta air strike on hospital kills 31, aid workers say
-
General strike hits planes, trains and services in Portugal

-
 Vietnam's capital chokes through week of toxic smog
Vietnam's capital chokes through week of toxic smog
-
Stocks mixed as US rate cut offset by Fed outlook, Oracle earnings

-
 Mexico approves punishing vape sales with jail time
Mexico approves punishing vape sales with jail time
-
Desert dunes beckon for Afghanistan's 4x4 fans

-
 Myanmar junta air strike on hospital kills 31: aid worker
Myanmar junta air strike on hospital kills 31: aid worker
-
British porn star faces Bali deportation after studio raid

-
 US, Japan hold joint air exercise after China-Russia patrols
US, Japan hold joint air exercise after China-Russia patrols
-
Skydiver survives plane-tail dangling incident in Australia

-
 Filipino typhoon survivors sue Shell over climate change
Filipino typhoon survivors sue Shell over climate change
-
Eurogroup elects new head as Russian frozen assets debate rages

-
 Thunder demolish Suns, Spurs shock Lakers to reach NBA Cup semis
Thunder demolish Suns, Spurs shock Lakers to reach NBA Cup semis
-
Fighting rages along Cambodia-Thailand border ahead of expected Trump call

-
 Hay fifty on debut helps put New Zealand on top in West Indies Test
Hay fifty on debut helps put New Zealand on top in West Indies Test
-
Taiwan to keep production of 'most advanced' chips at home: deputy FM

-
 Warmer seas, heavier rains drove Asia floods: scientists
Warmer seas, heavier rains drove Asia floods: scientists
-
Ex-Man Utd star Lingard scores on tearful farewell to South Korea

-
 Hay fifty on debut helps New Zealand to 73-run lead against West Indies
Hay fifty on debut helps New Zealand to 73-run lead against West Indies
-
South Korea minister resigns over alleged bribes from church

-
 Yemeni city buckles under surge of migrants seeking safety, work
Yemeni city buckles under surge of migrants seeking safety, work
-
Breakout star: teenage B-girl on mission to show China is cool

-
 Chocolate prices high before Christmas despite cocoa fall
Chocolate prices high before Christmas despite cocoa fall
-
Debut fifty for Hay takes New Zealand to 200-5 in West Indies Test

-
 Sweet 16 as Thunder demolish Suns to reach NBA Cup semis
Sweet 16 as Thunder demolish Suns to reach NBA Cup semis
-
Austria set to vote on headscarf ban in schools

-
 Asian traders cheer US rate cut but gains tempered by outlook
Asian traders cheer US rate cut but gains tempered by outlook
-
Racing towards great white sharks in Australia

-
 Fighting rages at Cambodia-Thailand border ahead of expected Trump call
Fighting rages at Cambodia-Thailand border ahead of expected Trump call
-
Venezuelan opposition leader emerges from hiding after winning Nobel

-
 Eddie Jones given Japan vote of confidence for 2027 World Cup
Eddie Jones given Japan vote of confidence for 2027 World Cup
-
Kennedy's health movement turns on Trump administration over pesticides


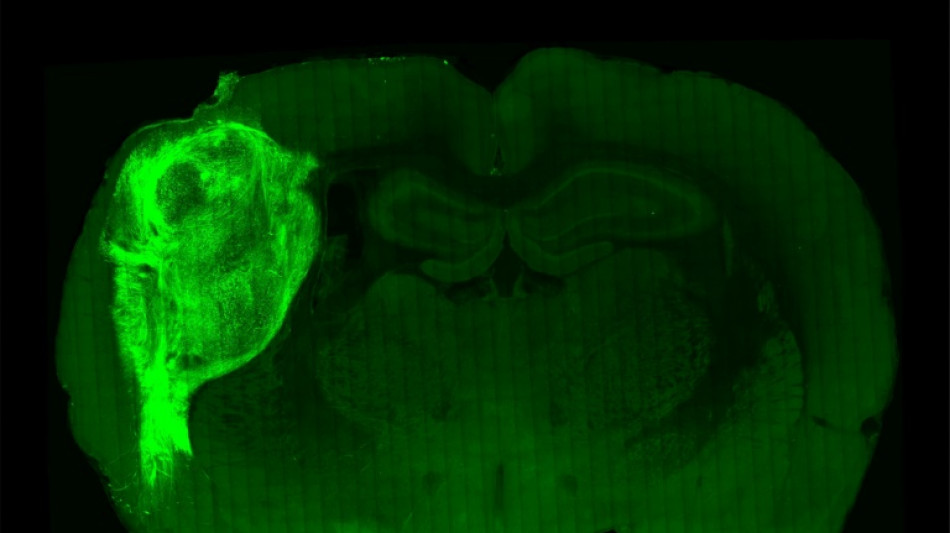
Human brain cells implanted in rats offer research gold mine
Scientists have successfully implanted and integrated human brain cells into newborn rats, creating a new way to study complex psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and autism, and perhaps eventually test treatments.
Studying how these conditions develop is incredibly difficult -- animals do not experience them like people, and humans cannot simply be opened up for research.
Scientists can assemble small sections of human brain tissue derived from stem cells in petri dishes, and have already done so with more than a dozen brain regions.
But in dishes, "neurons don't grow to the size which a human neuron in an actual human brain would grow", said Sergiu Pasca, the study's lead author and professor of psychiatry and behavioural sciences at Stanford University.
And isolated from a body, they cannot tell us what symptoms a defect will cause.
To overcome those limitations, researchers implanted the groupings of human brain cells, called organoids, into the brains of young rats.
The rats' age was important: human neurons have been implanted into adult rats before, but an animal's brain stops developing at a certain age, limiting how well implanted cells can integrate.
"By transplanting them at these early stages, we found that these organoids can grow relatively large, they become vascularised (receive nutrients) by the rat, and they can cover about a third of a rat's (brain) hemisphere," Pasca said.
- Ethical dilemmas -
To test how well the human neurons integrated with the rat brains and bodies, air was puffed across the animals' whiskers, which prompted electrical activity in the human neurons.
That showed an input connection -- external stimulation of the rat's body was processed by the human tissue in the brain.
The scientists then tested the reverse: could the human neurons send signals back to the rat's body?
They implanted human brain cells altered to respond to blue light, and then trained the rats to expect a "reward" of water from a spout when blue light shone on the neurons via a cable in the animals' skulls.
After two weeks, pulsing the blue light sent the rats scrambling to the spout, according to the research published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
The team has now used the technique to show that organoids developed from patients with Timothy syndrome grow more slowly and display less electrical activity than those from healthy people.
The technique could eventually be used to test new drugs, according to J. Gray Camp of the Roche Institute for Translational Bioengineering, and Barbara Treutlein of ETH Zurich.
It "takes our ability to study human brain development, evolution and disease into uncharted territory", the pair, who were not involved in the study, wrote in a review commissioned by Nature.
The method raises potentially uncomfortable questions -- how much human brain tissue can be implanted into a rat before the animal's nature is changed? Would the method be ethical in primates?
Pasca argued that limitations on how deeply human neurons integrate with the rat brain provide "natural barriers".
Rat brains develop much faster than human ones, "so there's only so much that the rat cortex can integrate".
But in species closer to humans, those barriers might no longer exist, and Pasca said he would not support using the technique in primates for now.
He argued though that there is a "moral imperative" to find ways to better study and treat psychiatric disorders.
"Certainly the more human these models are becoming, the more uncomfortable we feel," he said.
But "human psychiatric disorders are to a large extent uniquely human. So we're going to have to think very carefully... how far we want to go with some of these models moving forward."
J.Horn--BTB




