
-
 Burkinabe teen behind viral French 'coup' video has no regrets
Burkinabe teen behind viral French 'coup' video has no regrets
-
Brazil court rejects new Bolsonaro appeal against coup conviction

-
 Three-time Grand Slam winner Wawrinka to retire in 2026
Three-time Grand Slam winner Wawrinka to retire in 2026
-
Man Utd can fight for Premier League title in next few years: Amorim

-
 Pandya blitz powers India to T20 series win over South Africa
Pandya blitz powers India to T20 series win over South Africa
-
Misinformation complicated Brown University shooting probe: police

-
 IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
-
US halts green card lottery after MIT professor, Brown University killings

-
 Stocks advance as markets cheer weak inflation
Stocks advance as markets cheer weak inflation
-
Emery says rising expectations driving red-hot Villa

-
 Three killed in Taipei metro attacks, suspect dead
Three killed in Taipei metro attacks, suspect dead
-
Seven Colombian soldiers killed in guerrilla attack: army

-
 Amorim takes aim at Man Utd youth stars over 'entitlement'
Amorim takes aim at Man Utd youth stars over 'entitlement'
-
Mercosur meets in Brazil, EU eyes January 12 trade deal

-
 US Fed official says no urgency to cut rates, flags distorted data
US Fed official says no urgency to cut rates, flags distorted data
-
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain

-
 Spurs 'not a quick fix' for under-fire Frank
Spurs 'not a quick fix' for under-fire Frank
-
Poland president accuses Ukraine of not appreciating war support

-
 Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
-
Amorim unfazed by 'Free Mainoo' T-shirt ahead of Villa clash

-
 PSG penalty hero Safonov ended Intercontinental win with broken hand
PSG penalty hero Safonov ended Intercontinental win with broken hand
-
French court rejects Shein suspension
-
 'It's so much fun,' says Vonn as she milks her comeback
'It's so much fun,' says Vonn as she milks her comeback
-
Moscow intent on pressing on in Ukraine: Putin

-
 UN declares famine over in Gaza, says 'situation remains critical'
UN declares famine over in Gaza, says 'situation remains critical'
-
Guardiola 'excited' by Man City future, not pondering exit

-
 Zabystran upsets Odermatt to claim first World Cup win in Val Gardena super-G
Zabystran upsets Odermatt to claim first World Cup win in Val Gardena super-G
-
Czechs name veteran coach Koubek for World Cup play-offs

-
 PSG penalty hero Safonov out until next year with broken hand
PSG penalty hero Safonov out until next year with broken hand
-
Putin says ball in court of Russia's opponents in Ukraine talks

-
 Czech Zabystran upsets Odermatt to claim Val Gardena super-G
Czech Zabystran upsets Odermatt to claim Val Gardena super-G
-
NGOs fear 'catastrophic impact' of new Israel registration rules

-
 US suspends green card lottery after MIT professor, Brown University killings
US suspends green card lottery after MIT professor, Brown University killings
-
Stocks mixed with focus on central banks, tech

-
 Arsenal in the 'right place' as Arteta marks six years at club
Arsenal in the 'right place' as Arteta marks six years at club
-
Sudan's El-Fasher under the RSF, destroyed and 'full of bodies'

-
 From farms to court, climate-hit communities take on big polluters
From farms to court, climate-hit communities take on big polluters
-
Liverpool have 'moved on' from Salah furore, says upbeat Slot

-
 Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant
Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant
-
Iraq negotiates new coalition under US pressure

-
 France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
-
Putin hails Ukraine gains, threatens more, in annual press conference

-
 US suspends green card lottery after Brown, MIT professor shootings
US suspends green card lottery after Brown, MIT professor shootings
-
Chelsea's Maresca says Man City link '100 percent' speculation

-
 Dominant Head moves into Bradman territory with fourth Adelaide ton
Dominant Head moves into Bradman territory with fourth Adelaide ton
-
Arsenal battle to stay top of Christmas charts

-
 Mexican low-cost airlines Volaris and Viva agree to merger
Mexican low-cost airlines Volaris and Viva agree to merger
-
Border casinos caught in Thailand-Cambodia crossfire

-
 Australia's Head slams unbeaten 142 to crush England's Ashes hopes
Australia's Head slams unbeaten 142 to crush England's Ashes hopes
-
Epstein files due as US confronts long-delayed reckoning


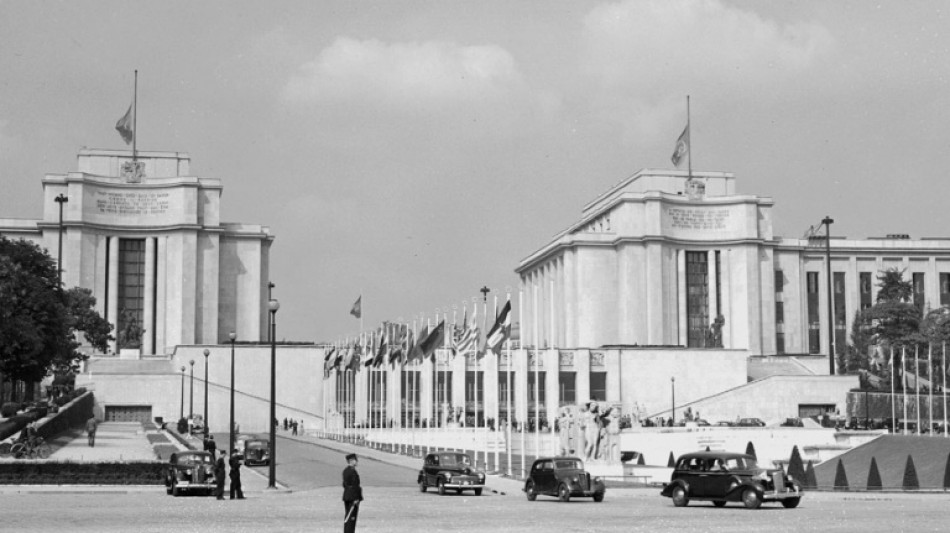
Universal Declaration of Human Rights turns 75
On December 10, 1948, the United Nations adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in the hope of creating a better world after the horrors of World War II.
Coming three years after the Allied victory over the Nazis, it was the first time that countries had agreed to protect fundamental rights and freedoms on a universal scale, for all people.
It was also one of the first achievements of the United Nations, itself born from the ashes of the Second World War, and inspired the development of international human rights law.
Its adoption in Paris was hailed with a lengthy standing ovation from delegates determined that the world would never again see the likes of Auschwitz, Hiroshima and other atrocities.
Although not legally binding, the declaration stresses the supremacy of individual rights over those of states.
It puts economic, social and cultural freedoms on the same level as civil and political rights.
Human rights were no longer exclusively an internal affair, as Hitler had claimed to prevent foreign interference. They were now a universal issue.
On the 75th anniversary of the adoption of the milestone charter, here is some historical background.
- Divided world seeks consensus -
The UN's first General Assembly in 1946 created a Commission on Human Rights -- made up of 18 members from various political, cultural and religious backgrounds -- to work on an international bill of rights.
The drafting committee first met in 1947 under the dynamic chairmanship of Eleanor Roosevelt, widow of the US president Franklin D. Roosevelt.
Its other representatives were from eight countries selected according to their geographical location, with Canada's John Peters Humphrey and France’s Rene Cassin playing key roles in the drafting.
"It is the first document of an ethical sort that organised humanity has ever adopted," recalled Cassin.
It was inspired by the principles behind the United States Declaration of Independence of 1776 and France’s Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen of 1789.
Several women played key roles in the drafting, namely Hansa Mehta, a fervent advocate of women's rights in India and abroad.
She is widely credited with changing Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights from "All men are born free and equal" to "All human beings are born free and equal".
The declaration was adopted by the UN's third General Assembly in Paris on December 10, 1948.
It was supported by 48 of the UN's then 58 member countries.
Two others -- Yemen and Honduras -- were absent.
The remaining eight abstained -- Belarus, Czechoslovakia, Poland, the Soviet Union, Ukraine, Yugoslavia, apartheid South Africa and Saudi Arabia, which challenged the notion that men and women were equal.
- Inspiring but contested -
"At a time when the world was divided into Eastern and Western blocs, finding a common ground on what should make the essence of the document proved to be a colossal task," the UN says on its website.
Communists said there was an over-emphasis on individual and political rights at the expense of social rights.
Western democracies were wary of the declaration becoming a restrictive legal tool that could be used against them by their own their colonies.
Despite the doubts and debates at the time, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights inspired all post-war treaties and is regarded as the foundation of international human rights law.
The international conventions against the discrimination of women in 1979 and against torture in 1984; the rights of children in 1990; the creation of the International Criminal Court in 1998 -- all are its direct descendants.
It also inspired the "right to intervene" in another country on humanitarian grounds, as championed by former French foreign minister Bernard Kouchner, who co-founded Doctors Without Borders (MSF).
But the declaration has not been able to prevent violations of the rights it espouses.
Nor has it escaped criticism, including that the concept of "universalism" is little more than a Western diktat.
And it has met ideological, cultural and religious resistance from various countries, such as China and Russia as well as those that apply Islamic Sharia law.
Seventy-five years after its adoption, there are calls for the declaration to be updated, for example, to incorporate challenges such as climate change, mass migration and modern technologies.
Bur-cf-ccd-rap/mw/eab/gil/bp
L.Janezki--BTB




