-
 CK Hutchison launches arbitration over Panama Canal port ruling
CK Hutchison launches arbitration over Panama Canal port ruling
-
Stocks mostly rise as traders ignore AI-fuelled sell-off on Wall St

-
 Acclaimed Iraqi film explores Saddam Hussein's absurd birthday rituals
Acclaimed Iraqi film explores Saddam Hussein's absurd birthday rituals
-
On rare earth supply, Trump for once seeks allies

-
 Ukrainian chasing sumo greatness after meteoric rise
Ukrainian chasing sumo greatness after meteoric rise
-
Draper to make long-awaited return in Davis Cup qualifier

-
 Can Ilia Malinin fulfil his promise at the Winter Olympics?
Can Ilia Malinin fulfil his promise at the Winter Olympics?
-
CK Hutchison begins arbitration against Panama over annulled canal contract

-
 UNESCO recognition inspires hope in Afghan artist's city
UNESCO recognition inspires hope in Afghan artist's city
-
Ukraine, Russia, US negotiators gather in Abu Dhabi for war talks

-
 WTO must 'reform or die': talks facilitator
WTO must 'reform or die': talks facilitator
-
Doctors hope UK archive can solve under-50s bowel cancer mystery

-
 Stocks swing following latest AI-fuelled sell-off on Wall St
Stocks swing following latest AI-fuelled sell-off on Wall St
-
Demanding Dupont set to fire France in Ireland opener

-
 Britain's ex-prince Andrew leaves Windsor home: BBC
Britain's ex-prince Andrew leaves Windsor home: BBC
-
Coach plots first South Africa World Cup win after Test triumph

-
 Spin-heavy Pakistan hit form, but India boycott risks early T20 exit
Spin-heavy Pakistan hit form, but India boycott risks early T20 exit
-
Japan eyes Premier League parity by aligning calendar with Europe

-
 Whack-a-mole: US academic fights to purge his AI deepfakes
Whack-a-mole: US academic fights to purge his AI deepfakes
-
Love in a time of war for journalist and activist in new documentary

-
 'Unprecedented mass killing': NGOs battle to quantify Iran crackdown scale
'Unprecedented mass killing': NGOs battle to quantify Iran crackdown scale
-
Seahawks kid Cooper Kupp seeks new Super Bowl memories

-
 Thousands of Venezuelans march to demand Maduro's release
Thousands of Venezuelans march to demand Maduro's release
-
AI, manipulated images falsely link some US politicians with Epstein

-
 Move on, says Trump as Epstein files trigger probe into British politician
Move on, says Trump as Epstein files trigger probe into British politician
-
Arteta backs Arsenal to build on 'magical' place in League Cup final

-
 Evil Empire to underdogs: Patriots eye 7th Super Bowl
Evil Empire to underdogs: Patriots eye 7th Super Bowl
-
UBS grilled on Capitol Hill over Nazi-era probe

-
 Guardiola 'hurt' by suffering caused in global conflicts
Guardiola 'hurt' by suffering caused in global conflicts
-
Marseille do their work early to beat Rennes in French Cup

-
 Colombia's Petro, Trump hail talks after bitter rift
Colombia's Petro, Trump hail talks after bitter rift
-
Trump signs spending bill ending US government shutdown

-
 Arsenal sink Chelsea to reach League Cup final
Arsenal sink Chelsea to reach League Cup final
-
Leverkusen sink St Pauli to book spot in German Cup semis

-
 'We just need something positive' - Monks' peace walk across US draws large crowds
'We just need something positive' - Monks' peace walk across US draws large crowds
-
Milan close gap on Inter with 3-0 win over Bologna

-
 No US immigration agents at Super Bowl: security chief
No US immigration agents at Super Bowl: security chief
-
NASA Moon mission launch delayed to March after test

-
 'You are great': Trump makes up with Colombia's Petro in fireworks-free meeting
'You are great': Trump makes up with Colombia's Petro in fireworks-free meeting
-
Spain to seek social media ban for under-16s

-
 X hits back after France summons Musk, raids offices in deepfake probe
X hits back after France summons Musk, raids offices in deepfake probe
-
LIV Golf events to receive world ranking points: official

-
 Russia resumes large-scale Ukraine strikes in glacial weather
Russia resumes large-scale Ukraine strikes in glacial weather
-
US House passes spending bill ending government shutdown

-
 US jet downs Iran drone but talks still on course
US jet downs Iran drone but talks still on course
-
UK police launching criminal probe into ex-envoy Mandelson

-
 US-Iran talks 'still scheduled' after drone shot down: White House
US-Iran talks 'still scheduled' after drone shot down: White House
-
Chomsky sympathized with Epstein over 'horrible' press treatment

-
 French prosecutors stick to demand for five-year ban for Le Pen
French prosecutors stick to demand for five-year ban for Le Pen
-
Russia's economic growth slowed to 1% in 2025: Putin


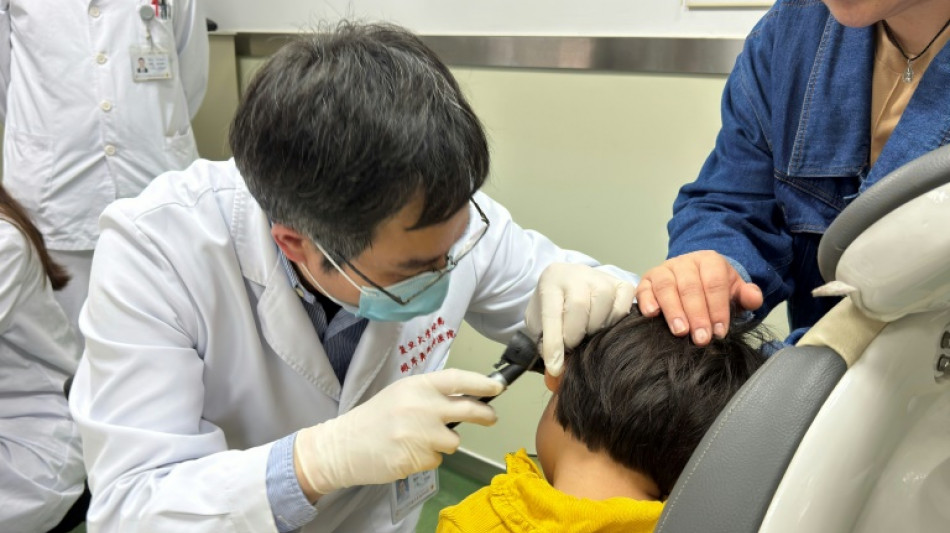
'Whole family cried': New gene therapy offers hope for deaf kids
Zhu Yangyang babbles away like a typical happy three-year-old, calling out for "mama" and "papa" and accurately naming colors -- a remarkable achievement considering he was completely deaf just months ago.
He is one of five children whose hearing was restored through a revolutionary new gene therapy in a clinical trial led by Chinese and American researchers, offering new hope for those born with a rare genetic mutation.
Yangyang's mother Chang Yiyi says she was moved to tears when she realized, around three weeks after the treatment last September, that Yangyang could hear her knocking on the door.
"I hid in a closet and called for him, and he still responded!" she told AFP in an interview from Shanghai.
The results of the study, published Wednesday in the prestigious journal Nature Medicine, mark the first time the procedure was performed on both ears. This led to significant improvements in speech perception and the ability to locate the source of sounds compared to treatment in just one ear.
"This is absolutely a turning point," Zheng-Yi Chen, the study's senior author at the Eaton-Peabody Laboratories at Mass Eye and Ear, told AFP, adding companies are now conducting clinical trials, including two in Boston, with the goal of moving towards regulatory approval.
"If the results hold, without any complications, I think in three to five years, it may be a medically approved product," he added.
- Rare mutation -
There are around 26 million people globally with genetic forms of deafness, with this particular therapy focusing on people born with a mutation of the OTOF gene -- roughly two to eight percent of inherited deafness cases.
This defect means they are unable to produce the protein otoferlin, which is needed for hair cells in the inner ear to convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that can be sent to the brain.
The treatment involves injecting a modified virus into the inner ear that smuggles in a working version of the OTOF gene, restoring hearing.
When they realized that Yangyang could hear for the first time, "the whole family cried" including Yangyang's mother and grandmother, said lead study author Yilai Shu of the Eye & ENT Hospital of Fudan University in Shanghai.
Chang, a 26-year-old homemaker, said that taking care of her son has become much easier since he began developing language skills, and the family soon hopes to move him from a speech rehabilitation school to traditional kindergarten.
- More genetic targets -
Shu led the research team that delivered the very first OTOF gene therapy in 2022, pioneering a treatment that has since been administered to more children around the world, including in the United States and the United Kingdom.
Treating both ears presented new challenges, he told AFP. Doubling the surgical procedures increased the risk of side effects.
However, careful dosing minimized the immune response, and only mild to moderate side effects -- like fever, vomiting and slightly elevated white cell counts -- were observed.
All five children, who ranged in age from one to 11, saw major improvements.
Two of them gained an ability to appreciate music -- a more complex acoustic signal -- and danced happily in videos recorded for the study.
Surprisingly, even the 11-year-old has gained some capacity to understand speech and talk, even though it was expected it would be too late for the brain to acquire this ability if it had never before perceived sound.
"That really shows our brain has a plasticity that maybe lasts much longer than we originally thought," said Chen. The clinical trial is ongoing, and the participants will be monitored for long-term follow up.
Meanwhile, Shu and Chen said they are working on further animal testing to develop treatments for other causes of genetic deafness, including those related to the GJB2 gene -- the most common cause of deafness present at birth.
F.Pavlenko--BTB



