-
 Cuban tourism in crisis; visitors repelled by fuel, power shortages
Cuban tourism in crisis; visitors repelled by fuel, power shortages
-
Liverpool set for Jacquet deal, Palace sign Strand Larsen on deadline day

-
 FIFA president Infantino defends giving peace prize to Trump
FIFA president Infantino defends giving peace prize to Trump
-
Trump cuts India tariffs, says Modi will stop buying Russian oil

-
 Borthwick backs Itoje to get 'big roar' off the bench against Wales
Borthwick backs Itoje to get 'big roar' off the bench against Wales
-
Twenty-one friends from Belgian village win €123mn jackpot

-
 Mateta move to Milan scuppered by medical concerns: source
Mateta move to Milan scuppered by medical concerns: source
-
Late-January US snowstorm wasn't historically exceptional: NOAA

-
 Punctuality at Germany's crisis-hit railway slumps
Punctuality at Germany's crisis-hit railway slumps
-
Gazans begin crossing to Egypt for treatment after partial Rafah reopening

-
 Halt to MSF work will be 'catastrophic' for people of Gaza: MSF chief
Halt to MSF work will be 'catastrophic' for people of Gaza: MSF chief
-
Italian biathlete Passler suspended after pre-Olympics doping test

-
 Europe observatory hails plan to abandon light-polluting Chile project
Europe observatory hails plan to abandon light-polluting Chile project
-
Iran president orders talks with US as Trump hopeful of deal

-
 Uncertainty grows over when US budget showdown will end
Uncertainty grows over when US budget showdown will end
-
Oil slides, gold loses lustre as Iran threat recedes

-
 Russian captain found guilty in fatal North Sea crash
Russian captain found guilty in fatal North Sea crash
-
Disney earnings boosted by theme parks, as CEO handover nears

-
 Sri Lanka drop Test captain De Silva from T20 World Cup squad
Sri Lanka drop Test captain De Silva from T20 World Cup squad
-
France demands 1.7 bn euros in payroll taxes from Uber: media report

-
 EU will struggle to secure key raw materials supply, warns report
EU will struggle to secure key raw materials supply, warns report
-
France poised to adopt 2026 budget after months of tense talks

-
 Latest Epstein file dump rocks UK royals, politics
Latest Epstein file dump rocks UK royals, politics
-
Arteta seeks Arsenal reinforcement for injured Merino

-
 Russia uses sport to 'whitewash' its aggression, says Ukraine minister
Russia uses sport to 'whitewash' its aggression, says Ukraine minister
-
Chile officially backs Bachelet candidacy for UN top job

-
 European stocks rise as oil tumbles, while tech worries weigh on New York
European stocks rise as oil tumbles, while tech worries weigh on New York
-
England captain Itoje on bench for Six Nations opener against Wales

-
 Rahm says golfers should be 'free' to play where they want after LIV defections
Rahm says golfers should be 'free' to play where they want after LIV defections
-
More baby milk recalls in France after new toxin rules

-
 Rosenior will not rush Estevao return from Brazil
Rosenior will not rush Estevao return from Brazil
-
Mercedes ready to win F1 world title, says Russell

-
 Germany hit by nationwide public transport strike
Germany hit by nationwide public transport strike
-
Barca coach Flick 'not happy' with Raphinha thigh strain

-
 WHO chief says turmoil creates chance for reset
WHO chief says turmoil creates chance for reset
-
European stocks rise as gold, oil prices tumble

-
 Rink issues resolved, NHL stars chase Olympic gold at Milan
Rink issues resolved, NHL stars chase Olympic gold at Milan
-
S. Korea celebrates breakthrough K-pop Grammy win for 'Golden'

-
 Rodri rages that officials 'don't want' Man City to win
Rodri rages that officials 'don't want' Man City to win
-
Gaza's Rafah crossing makes limited reopening after two-year war

-
 African players in Europe: Ouattara dents Villa title hopes
African players in Europe: Ouattara dents Villa title hopes
-
Liverpool beat Chelsea to Rennes defender Jacquet - reports

-
 S. Korea celebrates breakthrough Grammy win for K-pop's 'Golden'
S. Korea celebrates breakthrough Grammy win for K-pop's 'Golden'
-
Trump says US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba

-
 Trump threatens legal action against Grammy host over Epstein comment
Trump threatens legal action against Grammy host over Epstein comment
-
Olympic Games in northern Italy have German twist

-
 Bad Bunny: the Puerto Rican phenom on top of the music world
Bad Bunny: the Puerto Rican phenom on top of the music world
-
Snapchat blocks 415,000 underage accounts in Australia

-
 At Grammys, 'ICE out' message loud and clear
At Grammys, 'ICE out' message loud and clear
-
Dalai Lama's 'gratitude' at first Grammy win

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.04% | 23.75 | $ | |
| RIO | 1.4% | 92.325 | $ | |
| CMSD | 0.15% | 24.085 | $ | |
| AZN | -1.86% | 186.965 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 0.12% | 82.5 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.57% | 61.025 | $ | |
| NGG | -1.03% | 84.4 | $ | |
| GSK | 1.42% | 52.345 | $ | |
| BCC | 1.28% | 81.86 | $ | |
| RYCEF | 4.19% | 16.7 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.3% | 25.783 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.53% | 13.15 | $ | |
| RELX | -0.75% | 35.535 | $ | |
| BP | -0.37% | 37.74 | $ | |
| VOD | 1.88% | 14.93 | $ |

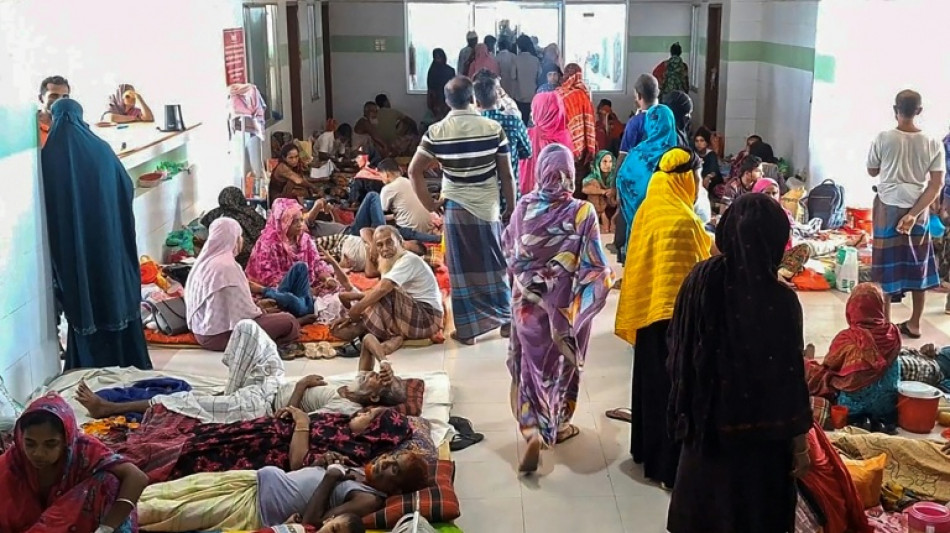
Deadly dengue fever impacts climate-hit Bangladesh coast
Mosquito-borne dengue fever was rarely a major problem in Bangladesh's coastal districts, but some hospitals are so full of those with the potentially deadly virus that patients are treated on the floor.
As climate change drives erratic weather patterns, experts point to a dire lack of clean drinking water in the wider delta -- where the snaking Brahmaputra and Ganges rivers reach the sea -- as a likely driving force for the surge.
Rakibul Islam Rajan said his two-year-old daughter keeps searching for her mother, Azmeri Mona Lisa Zareen, who died of dengue in early June in the southern region of Barisal.
"Zareen developed high fever... her blood pressure collapsed -- and then she couldn't breathe," said 31-year-old Rajan.
"Our daughter keeps searching for her from one room to another".
In the worst cases, intense viral fevers trigger bleeding, internally or from the mouth and nose.
Barisal has recorded nearly half of the 7,500 dengue cases across Bangladesh this year, according to the Institute of Epidemiology, Disease Control and Research (IEDCR).
Five people have died there this year with dengue fever, out of 31 deaths recorded across the entire country of some 170 million people.
Numbers are still far below the deadly outbreak of 2023, when more than 1,700 people died across the South Asian nation, and more than 200,000 were infected.
In the Barisal district of Barguna, the hospital is packed full.
Barisal health chief Shyamol Krishna Mondal said it was the "worst we've seen".
Barguna's 250-bed public hospital was coping with more than 200 dengue patients.
"We couldn't even offer beds," Mondal said. "They are getting treatment while lying on the floor."
Kabirul Bashar, an expert on disease at Jahangirnagar University, said a lack of clean water was "one of the major reasons".
People store rainwater in containers, exactly the conditions mosquitoes love.
"The water distribution system is almost absent," Bashar said.
- 'Vulnerability is soaring' -
While a lack of clean water is a long-running problem, climate change is making it worse.
Rising seas driven by climate change threaten swathes of low-lying Bangladesh, with increasing numbers of powerful storms bringing seawater further inland, turning wells and lakes salty, according to government scientists.
Changing weather patterns, making once predictable rains uncertain, adds to the challenge -- with people storing rainwater when they can.
But Mushtuq Husain, a public health expert and adviser at IEDCR, said that the plentiful water storage pots also provided perfect mosquito breeding sites.
"We can't allow water stagnation anywhere -- that should be the rule of thumb, but it's not happening," he said.
"The vulnerability is soaring because of the high temperatures and erratic rainfall, which are conducive to mosquito breeding."
Bangladesh has recorded cases of dengue since the 1960s but documented its first outbreak of dengue haemorrhagic fever, a severe and sometimes fatal form of the disease, in 2000.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has warned that dengue and other mosquito-borne viruses are spreading faster and further due to climate change.
About half of the world's population is now at risk of dengue, with an estimated 100 to 400 million infections occurring each year, and many of those causing only mild illness, according to the WHO.
Rajan, mourning his wife, worries that there will be more deaths to come, accusing local authorities of failing to stem mosquitoes.
"Dengue has taken her," he said of his late wife. "I don't know how many more are in the queue... but I don't see enough cleanup activities."
C.Kovalenko--BTB