
-
 Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open
Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open
-
Exhibition of Franco-Chinese print master Zao Wou-Ki opens in Hong Kong

-
 Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike
Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike
-
Why SpaceX IPO plan is generating so much buzz

-
 Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls
Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls
-
US envoy to meet Zelensky, Europe leaders in Berlin this weekend

-
 North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
-
US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast

-
 Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
-
Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'

-
 Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
-
World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
-
Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga

-
 US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
-
UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026

-
 Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
-
Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings

-
 UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
-
Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung

-
 Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
-
NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit

-
 UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
-
Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?

-
 Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
-
Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats

-
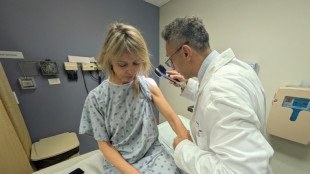 'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
-
Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win

-
 Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
-
Trump says Thailand, Cambodia have agreed to stop border clashes

-
 Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
-
Marseille coach tips Greenwood as 'potential Ballon d'Or'

-
 Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
-
Thai PM says asked Trump to press Cambodia on border truce

-
 Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
-
World stocks retrench, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
-
Trump attack on Europe migration 'disaster' masks toughening policies

-
 US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
-
'Chilling effect': Israel reforms raise press freedom fears

-
 Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
-
No doubting Man City boss Guardiola's passion says Toure

-
 Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
-
World stocks consolidate Fed-fuelled gains

-
 British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
-
Man Utd sweat on Africa Cup of Nations trio

-
 EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
-
Taylor Swift breaks down in Eras documentary over Southport attack

-
 Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
-
France updates net-zero plan, with fossil fuel phaseout


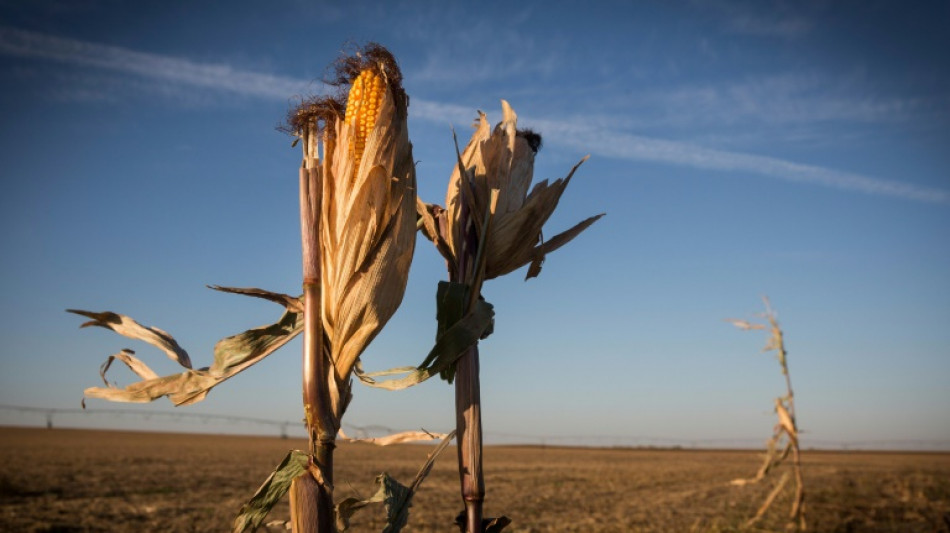
Farmers in US Midwest struggle amid prolonged drought
Months without rain have left farmers across the vast US Midwest, part of the country's essential "breadbasket," seeing crop yields in freefall, with some fields too damaged to harvest.
At the 4,000-acre (1,600-hectare) Tucker Farms in Venango, Nebraska, "we were only able to harvest... around 500" acres, most of it wheat, said Rachel Tucker.
Much of the rest had shriveled up under a relentlessly hot sun.
The drought has attracted grasshoppers, which threatened the flowers the Tuckers also grow -- until they brought in praying mantises to control the winged pests.
If the American West has been suffering through water shortages for years, the Midwest has not seen conditions this bad since 2012.
"It's even worse than 2012," said Tucker. "Much worse."
Her husband, whose grandfather farmed these same fields, says things have not been this bad since the so-called Dust Bowl days of the 1930s.
The story is just as grim to the south, in western Kansas.
"I was catching up with some older farmers this morning," said Marc Ramsey, whose family has farmed near the small town of Scott City for nearly a century.
"Guys that are in their 70s and 80s are saying, you know, they haven't even experienced anything like this in their lifetime. So it's pretty bad."
Rainfall has been almost nonexistent since late July, he said. Two inches "was all we've had, basically all year."
Rex Buchanan, director emeritus of the Kansas Geological Survey, said one thing seems different from the dry years of 2010-2012: "It seems like when the rain shut off, it just completely shut off."
- Dwindling groundwater -
Drought has hit the three major US crops: wheat, corn and soybeans, and the US Department of Agriculture recently had to lower its nationwide yield predictions.
Along With Kansas and Nebraska, the Midwestern state of South Dakota has also been hard-hit.
In normal times, these three states provide one-third of US winter wheat production, and one-fourth of the corn output.
Approximately 30 percent of Marc Ramsey's land is irrigated and, meaning that portion is doing better than his other fields. Tucker Farms' single irrigated field also fares better than the others.
But even some of Ramsey's irrigated fields are producing only 80 bushels of corn per acre, less than half the usual rate.
High levels of water usage have led to "pretty dramatic declines" in aquifers across western Kansas, Buchanan said, adding that farmers in some areas "have really struggled."
"They’ve seen some wells go dry. They’ve had to return to dryland farming," meaning without irrigation.
- 'You just worry' -
With water rights strictly limited, Buchanan said some farmers have banded together in agreements on more cautious use of subterranean water, drawing as much as 20 percent less than permitted.
Ramsey, like the Tuckers, carries crop insurance covering exceptional losses.
But a year like 2022 can push up premiums, which were already rising due to increased commodity costs.
Insurance "covers your cost of productivity, for the most part," Ramsey said. "And so we'll be here next year and try it again."
But insurance doesn't refill dwindling aquifers -- something that autumn rains usually take care of.
The lack of soil moisture "will be a concern going forward into winter and next spring without a change in what we are currently seeing," said Brian Fuchs, a climatologist with the National Drought Mitigation Center at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
Though Buchanan says that "there’s certainly an awareness (among farmers) about climate change," despite the political sensitivity of the subject in the United States.
Farming is always difficult and unpredictable work -- and in years like this, said farmer Rachel Tucker, "you just worry about the suicide rate."
"So I'm hoping that everybody can stay in high spirits, and hope for the best next year."
C.Kovalenko--BTB



