
-
 Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open
Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open
-
Exhibition of Franco-Chinese print master Zao Wou-Ki opens in Hong Kong

-
 Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike
Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike
-
Why SpaceX IPO plan is generating so much buzz

-
 Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls
Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls
-
US envoy to meet Zelensky, Europe leaders in Berlin this weekend

-
 North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
-
US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast

-
 Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
-
Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'

-
 Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
-
World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
-
Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga

-
 US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
-
UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026

-
 Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
-
Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings

-
 UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
-
Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung

-
 Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
-
NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit

-
 UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
-
Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?

-
 Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
-
Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats

-
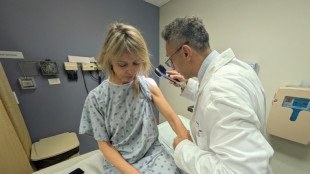 'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
-
Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win

-
 Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
-
Trump says Thailand, Cambodia have agreed to stop border clashes

-
 Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
-
Marseille coach tips Greenwood as 'potential Ballon d'Or'

-
 Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
-
Thai PM says asked Trump to press Cambodia on border truce

-
 Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
-
World stocks retrench, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
-
Trump attack on Europe migration 'disaster' masks toughening policies

-
 US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
-
'Chilling effect': Israel reforms raise press freedom fears

-
 Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
-
No doubting Man City boss Guardiola's passion says Toure

-
 Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
-
World stocks consolidate Fed-fuelled gains

-
 British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
-
Man Utd sweat on Africa Cup of Nations trio

-
 EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
-
Taylor Swift breaks down in Eras documentary over Southport attack

-
 Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
-
France updates net-zero plan, with fossil fuel phaseout


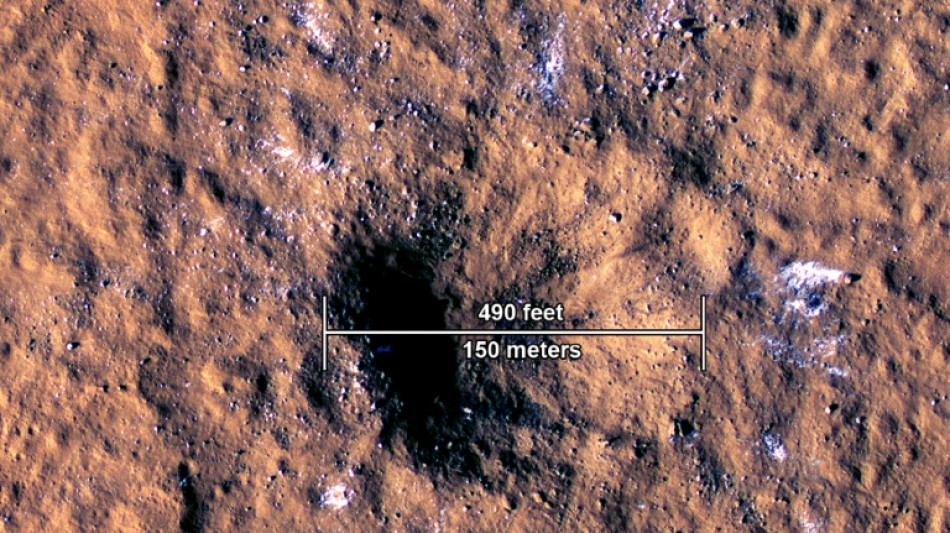
Meteorite that smashed into Mars shook planet, NASA says
Scientists who study Mars on Thursday revealed the remarkable Christmas gift they received from the planet last year.
On December 24, 2021, a meteorite hit Mars' surface, triggering magnitude 4 tremors, which were detected by NASA's InSight spacecraft -- which landed on the planet four years ago -- some 2,200 miles (3,500 kilometers) away.
The true origin of this so-called marsquake was only confirmed when the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) was able to take a picture of the newly formed crater created by the hit when it flew over the impact site less than 24 hours later.
The image is impressive, showing blocks of ice that were spewed up onto the planet's surface around the 492-foot (150-meter) wide and 70-foot (21-meter) deep hole.
The crater is the largest ever observed since the MRO began its Mars orbit 16 years ago.
And though meteorite impacts on Mars are not rare, "we never thought we'd see anything that big," Ingrid Daubar, who works on the InSight and MRO missions, told reporters at a press conference Thursday.
Researchers estimate that the meteorite itself would have measured between 16 to 39 feet across. An object of that size would have disintegrated in Earth's atmosphere before falling to the ground here.
"It is simply the biggest meteorite impact on the ground that we have heard since science has been done with seismographs or seismometers," said planetology professor Philippe Lognonne, who participated in two studies related to the observation published in the journal Science Thursday.
NASA released an audio recording of the collision, which was made by speeding up the vibrations collected by the seismometer.
- 'Useful' ice presence -
The valuable information gathered in studying the crash will contribute to deeper knowledge of Mars' interior and the history of how the planet was created, scientists said.
The presence of ice, in particular, is "surprising," said Daubar, who also co-authored the two studies.
"This is the warmest spot on Mars, the closest to the equator, we've ever seen water ice," she said.
In addition to the information this discovery offers about the Martian climate, the presence of water at this latitude -- and not just near the poles -- could prove "really useful" for future human visitors to Mars, director of NASA's Planetary Science Division Lori Glaze said.
"We'd want to land the astronauts as near to the equator as possible," she said, to take advantage of warmer temperatures.
"That ice could be converted into water, oxygen or hydrogen," Glaze said.
The impact was powerful enough to generate seismic waves both down to the planet's core and across its crust horizontally, making it possible to study Mars' internal structure -- revealing that the crust on which InSight sits is less dense than the crust the waves traveled over from the crater site.
The end of InSight's mission -- which recorded more than 1,300 marsquakes in total -- could come in the next couple of months, according to Bruce Banerdt of NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab, due to the expected accumulation of dust on the lander's solar power panel.
It's "sad," he said, while celebrating that the probe worked "marvelously" for four years.
H.Seidel--BTB



