
-
 Avatar 3 aims to become end-of-year blockbuster
Avatar 3 aims to become end-of-year blockbuster
-
Contenders plot path to 2026 World Cup glory after Trump steals show at draw

-
 Greaves leads dramatic West Indies run chase in NZ Test nail-biter
Greaves leads dramatic West Indies run chase in NZ Test nail-biter
-
World record-holders Walsh, Smith grab wins at US Open

-
 Ukraine, US to meet for third day, agree 'real progress' depends on Russia
Ukraine, US to meet for third day, agree 'real progress' depends on Russia
-
Double wicket strike as New Zealand eye victory over West Indies

-
 Peace medal and YMCA: Trump steals the show at World Cup draw
Peace medal and YMCA: Trump steals the show at World Cup draw
-
NBA legend Jordan in court as NASCAR anti-trust case begins

-
 How coaches reacted to 2026 World Cup draw
How coaches reacted to 2026 World Cup draw
-
Glasgow down Sale as Stomers win at Bayonne in Champions Cup

-
 Trump takes aim at Europe in new security strategy
Trump takes aim at Europe in new security strategy
-
Witness in South Africa justice-system crimes probe shot dead

-
 Tuchel urges England not to get carried away plotting route to World Cup glory
Tuchel urges England not to get carried away plotting route to World Cup glory
-
Russian ambassador slams EU frozen assets plan for Ukraine

-
 2026 World Cup draw is kind to favorites as Trump takes limelight
2026 World Cup draw is kind to favorites as Trump takes limelight
-
WHO chief upbeat on missing piece of pandemic treaty
-
 US vaccine panel upends hepatitis B advice in latest Trump-era shift
US vaccine panel upends hepatitis B advice in latest Trump-era shift
-
Ancelotti says Brazil have 'difficult' World Cup group with Morocco

-
 Kriecmayr wins weather-disrupted Beaver Creek super-G
Kriecmayr wins weather-disrupted Beaver Creek super-G
-
Ghostwriters, polo shirts, and the fall of a landmark pesticide study

-
 Mixed day for global stocks as market digest huge Netflix deal
Mixed day for global stocks as market digest huge Netflix deal
-
Fighting erupts in DR Congo a day after peace deal signed

-
 England boss Tuchel wary of 'surprise' in World Cup draw
England boss Tuchel wary of 'surprise' in World Cup draw
-
10 university students die in Peru restaurant fire

-
 'Sinners' tops Critics Choice nominations
'Sinners' tops Critics Choice nominations
-
Netflix's Warner Bros. acquisition sparks backlash

-
 France probes mystery drone flight over nuclear sub base
France probes mystery drone flight over nuclear sub base
-
Frank Gehry: five key works

-
 US Supreme Court to weigh Trump bid to end birthright citizenship
US Supreme Court to weigh Trump bid to end birthright citizenship
-
Frank Gehry, master architect with a flair for drama, dead at 96

-
 'It doesn't make sense': Trump wants to rename American football
'It doesn't make sense': Trump wants to rename American football
-
A day after peace accord signed, shelling forces DRC locals to flee

-
 Draw for 2026 World Cup kind to favorites as Trump takes center stage
Draw for 2026 World Cup kind to favorites as Trump takes center stage
-
Netflix to buy Warner Bros. in deal of the decade

-
 US sanctions equate us with drug traffickers: ICC dep. prosecutor
US sanctions equate us with drug traffickers: ICC dep. prosecutor
-
Migration and crime fears loom over Chile's presidential runoff

-
 French officer charged after police fracture woman's skull
French officer charged after police fracture woman's skull
-
Fresh data show US consumers still strained by inflation
-
 Eurovision reels from boycotts over Israel
Eurovision reels from boycotts over Israel
-
Trump takes centre stage as 2026 World Cup draw takes place

-
 Trump all smiles as he wins FIFA's new peace prize
Trump all smiles as he wins FIFA's new peace prize
-
US panel votes to end recommending all newborns receive hepatitis B vaccine

-
 Title favourite Norris reflects on 'positive' Abu Dhabi practice
Title favourite Norris reflects on 'positive' Abu Dhabi practice
-
Stocks consolidate as US inflation worries undermine Fed rate hopes

-
 Volcanic eruptions may have brought Black Death to Europe
Volcanic eruptions may have brought Black Death to Europe
-
Arsenal the ultimate test for in-form Villa, says Emery

-
 Emotions high, hope alive after Nigerian school abduction
Emotions high, hope alive after Nigerian school abduction
-
Another original Hermes Birkin bag sells for $2.86 mn

-
 11 million flock to Notre-Dame in year since rising from devastating fire
11 million flock to Notre-Dame in year since rising from devastating fire
-
Gymnast Nemour lifts lid on 'humiliation, tears' on way to Olympic gold


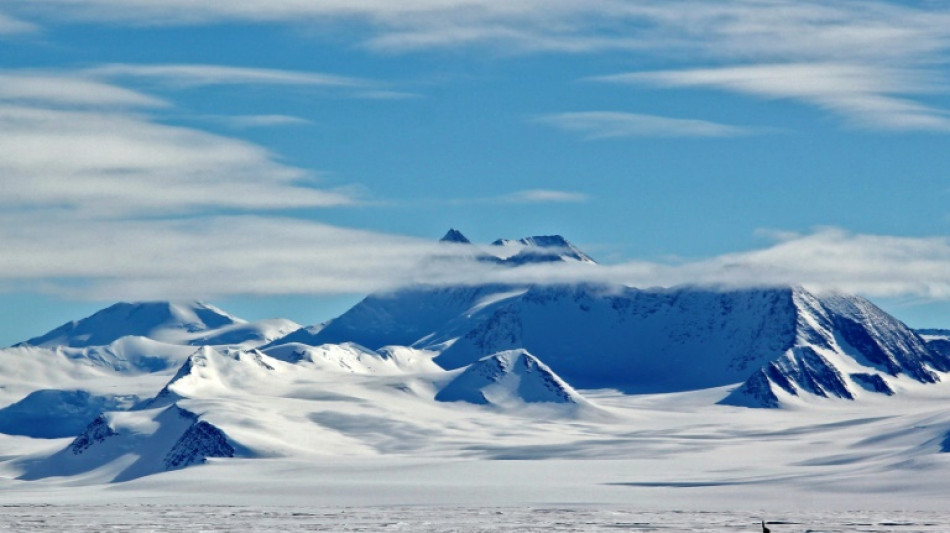
Sea ice in Antarctic at record low: US data center
Antarctic sea ice likely shrunk to a record low last week, US researchers said Monday, its lowest extent in the 45 years of satellite record-keeping.
The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the University of Colorado Boulder said that Antarctica's sea ice fell to 1.79 million square kilometers (691,000 million square miles) on February 21.
That exceeded the previous record low set in 2022 by 136,000 square kilometers (52,500 square miles).
NSIDC scientists stressed that the latest figure was preliminary since further late-season melt was still possible. They said they would issue a final number on the extent of ice in early March.
Melting sea ice exposes the thicker ice shelves buttressing Antarctica's ground ice sheet to waves and warmer temperatures.
Melting sea ice has no discernible impact on sea levels because the ice is already in ocean water.
But the sea ice rings Antarctica's massive ice shelves, the extensions of the freshwater glaciers that threaten catastrophic sea level rise over centuries if they continue melting as global temperatures rise.
"Antarctica's response to climate change has been different from the Arctic's," said Ted Scambos, a senior research scientist at the Cooperative Institute for Research in the Environmental Sciences (CIRES).
"The downward trend in sea ice may be a signal that global warming is finally affecting the floating ice around Antarctica, but it will take several more years to be confident of it," Scambos said.
The Antarctic cycle undergoes significant annual variations during its summers of thawing and winters of freezing, and the continent has not experienced the rapid melting of the past four decades that plague the ice sheets of Greenland and the Arctic due to global warming.
But the high melt rate since 2016 raises concerns that a significant downward trend may be taking hold.
Melting of the sea ice is problematic because it helps accelerate global warming.
When white sea ice -- which bounces up to 90 percent of the Sun's energy back into space -- is replaced by dark, unfrozen sea, the water absorbs a similar percentage of the Sun's heat instead.
Globally, last year was the fifth or sixth warmest on record despite the cooling influence of a natural La Nina weather pattern.
T.Bondarenko--BTB




