
-
 Rams ace Nacua apologizes over 'antisemitic' gesture furor
Rams ace Nacua apologizes over 'antisemitic' gesture furor
-
McIlroy wins BBC sports personality award for 2025 heroics

-
 Napoli beat Milan in Italian Super Cup semi-final
Napoli beat Milan in Italian Super Cup semi-final
-
Violence erupts in Bangladesh after wounded youth leader dies

-
 EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force
-
US hosting new Gaza talks to push next phase of deal

-
 Chicago Bears mulling Indiana home over public funding standoff
Chicago Bears mulling Indiana home over public funding standoff
-
Trump renames Kennedy arts center after himself

-
 Trump rebrands housing supplement as $1,776 bonuses for US troops
Trump rebrands housing supplement as $1,776 bonuses for US troops
-
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award

-
 Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care
-
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms

-
 Trump signs order reclassifying marijuana as less dangerous
Trump signs order reclassifying marijuana as less dangerous
-
Famed Kennedy arts center to be renamed 'Trump-Kennedy Center'

-
 US accuses S.Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
US accuses S.Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Wounded Bangladesh youth leader dies in Singapore hospital
Wounded Bangladesh youth leader dies in Singapore hospital
-
New photo dump fuels Capitol Hill push on Epstein files release

-
 Brazil, Mexico seek to defuse US-Venezuela crisis
Brazil, Mexico seek to defuse US-Venezuela crisis
-
Assange files complaint against Nobel Foundation over Machado win

-
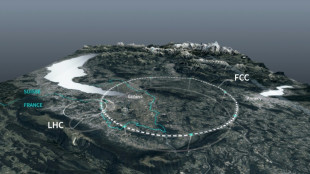 Private donors pledge $1 bn for CERN particle accelerator
Private donors pledge $1 bn for CERN particle accelerator
-
Russian court orders Austrian bank Raiffeisen to pay compensation

-
 US, Qatar, Turkey, Egypt to hold Gaza talks in Miami
US, Qatar, Turkey, Egypt to hold Gaza talks in Miami
-
Lula open to mediate between US, Venezuela to 'avoid armed conflict'

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US imposes sanctions on two more ICC judges for Israel probe

-
 US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
-
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty

-
 Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company
-
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce

-
 Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit
-
Pope replaces New York's Cardinal Dolan with pro-migrant bishop

-
 Odermatt takes foggy downhill for 50th World Cup win
Odermatt takes foggy downhill for 50th World Cup win
-
France exonerates women convicted over abortions before legalisation

-
 UK teachers to tackle misogyny in classroom
UK teachers to tackle misogyny in classroom
-
Historic Afghan cinema torn down for a mall

-
 US consumer inflation cools unexpectedly in November
US consumer inflation cools unexpectedly in November
-
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling

-
 ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future
-
Pope replaces New York's Cardinal Timothy Dolan with little-known bishop

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 Spain to buy 100 military helicopters from Airbus
Spain to buy 100 military helicopters from Airbus
-
US strike on alleged drug boat in Pacific kills four

-
 Thailand strikes building in Cambodia's border casino hub
Thailand strikes building in Cambodia's border casino hub
-
Protests in Bangladesh as India cites security concerns

-
 European stocks rise before central bank decisions on rates
European stocks rise before central bank decisions on rates
-
Tractors clog Brussels in anger at EU-Mercosur trade deal

-
 Not enough evidence against Swedish PM murder suspect: prosecutor
Not enough evidence against Swedish PM murder suspect: prosecutor
-
Nepal's ousted PM Oli re-elected as party leader


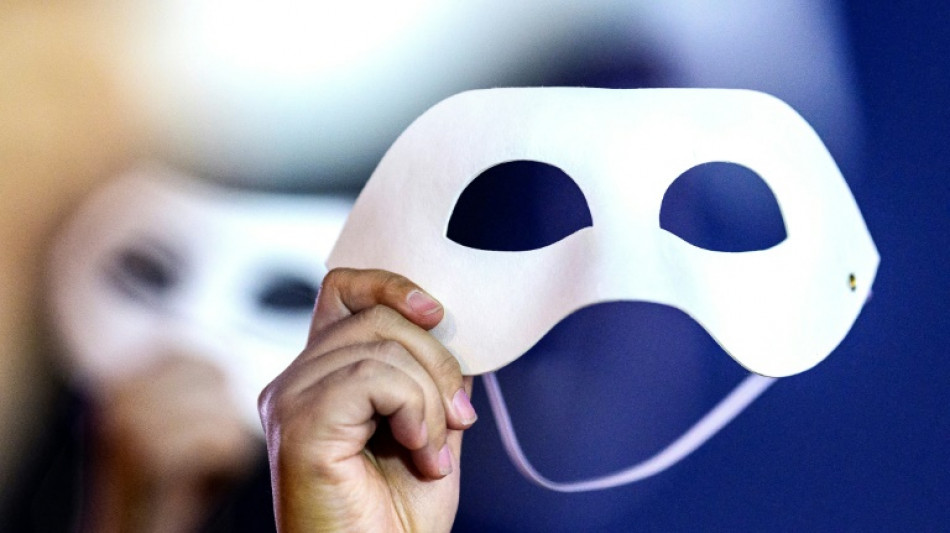
Tech firms fight to stem deepfake deluge
Tech firms are fighting the scourge of deepfakes, those deceptively realistic voices or videos used by scammers that are more available than ever thanks to artificial intelligence.
Ever-improving generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) tools have become weapons in the hands of bad actors intent on tricking people out of their money or even their identities.
Debby Bodkin tells of her 93-year-old mother receiving a telephone call, a cloned voice claiming, "It's me, mom... I've had an accident."
When asked where they were, the machine-made impersonator named a hospital.
Fortunately, it was a granddaughter who answered the phone, opting to hang up and call Bodkin at work where she was safe and well.
"It's not the first time scammers have called grandma," Bodkin told AFP. "It's daily."
Such deepfake phone scams typically go on to coax victims into paying for medical care or other made-up emergencies.
Used on social networks to hijack the notoriety of celebrities or other high-profile figures, sometimes for disinformation, deepfakes are also being exploited by criminal gangs.
Hong Kong police earlier this year revealed that a multinational firm employee was tricked into wiring HK$200 million (around US$26 million) to crooks who staged a videoconference with AI avatars of his colleagues.
A recent study by identification start-up iBoom found that a scant tenth of one percent of Americans and Britons were able to correctly tell when a picture or video was a deepfake.
A decade ago, there was a single AI tool for generating synthetic voices -- now there are hundreds of them, according to voice authentication specialist Vijay Balasubramaniyan, CEO of Pindrop Security.
GenAI has changed the game, he said.
"Before, it took 20 hours (of voice recording) to recreate your voice," the executive told AFP.
"Now, it's five seconds."
Firms such as Intel have stepped up with tools to detect GenAI-made audio or video in real-time.
Intel "FakeCatcher" detects color changes in facial blood vessels to distinguish genuine from bogus imagery.
Pindrop breaks down every second of audio and compares it with characteristics of a human voice.
"You have to keep up with the times," says Nicos Vekiarides, chief of Attestiv platform which specializes in authenticating digital creations.
"In the beginning, we saw people with six fingers on one hand, but progress has made it harder and harder to tell (deepfakes) with the naked eye."
- 'Global cybersecurity threat' -
Balasubramaniyan believes that software for spotting AI content will become standard at companies of all kinds.
While GenAI has blurred the boundary between human and machine, companies that re-establish that divide could soar in a market that will be worth billions of dollars, he said.
Vekiarides warned that the issue "is becoming a global cybersecurity threat."
"Any company can have its reputation tarnished by a deepfake or be targeted by these sophisticated attacks," Vekiarides said.
Balasubramaniyan added that the shift to telework provides more opportunity for bad actors to impersonate their way into companies.
Beyond the corporate world, many expect consumers to look for ways to fight off deepfake scams endangering their personal lives.
In January, China-based Honor unveiled a Magic7 smartphone with a built-in deepfake detector powered by AI.
British start-up Surf Security late last year launched a web browser that can flag synthetic voice or video, aiming it at businesses.
Siwei Lyu, a professor of computer science at the State University of New York at Buffalo, believes "deepfakes will become like spam," an internet nightmare that people eventually get under control.
"Those detection algorithms will be like spam filters in our email software," Lyu predicted.
"We're not there yet."
J.Bergmann--BTB



