
-
 Honduras begins partial vote recount in Trump-dominated election
Honduras begins partial vote recount in Trump-dominated election
-
Nike shares slump as China struggles continue

-
 Hundreds swim, float at Bondi Beach to honour shooting victims
Hundreds swim, float at Bondi Beach to honour shooting victims
-
Crunch time for EU leaders on tapping Russian assets for Ukraine

-
 Pope replaces New York's pro-Trump Cardinal with pro-migrant Chicagoan
Pope replaces New York's pro-Trump Cardinal with pro-migrant Chicagoan
-
Trump orders marijuana reclassified as less dangerous drug

-
 Rams ace Nacua apologizes over 'antisemitic' gesture furor
Rams ace Nacua apologizes over 'antisemitic' gesture furor
-
McIlroy wins BBC sports personality award for 2025 heroics

-
 Napoli beat Milan in Italian Super Cup semi-final
Napoli beat Milan in Italian Super Cup semi-final
-
Violence erupts in Bangladesh after wounded youth leader dies

-
 EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force
-
US hosting new Gaza talks to push next phase of deal

-
 Chicago Bears mulling Indiana home over public funding standoff
Chicago Bears mulling Indiana home over public funding standoff
-
Trump renames Kennedy arts center after himself

-
 Trump rebrands housing supplement as $1,776 bonuses for US troops
Trump rebrands housing supplement as $1,776 bonuses for US troops
-
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award

-
 Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care
-
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms

-
 Trump signs order reclassifying marijuana as less dangerous
Trump signs order reclassifying marijuana as less dangerous
-
Famed Kennedy arts center to be renamed 'Trump-Kennedy Center'

-
 US accuses S.Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
US accuses S.Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Wounded Bangladesh youth leader dies in Singapore hospital
Wounded Bangladesh youth leader dies in Singapore hospital
-
New photo dump fuels Capitol Hill push on Epstein files release

-
 Brazil, Mexico seek to defuse US-Venezuela crisis
Brazil, Mexico seek to defuse US-Venezuela crisis
-
Assange files complaint against Nobel Foundation over Machado win

-
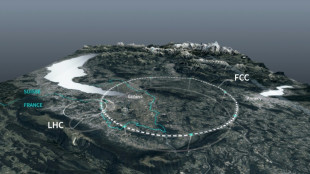 Private donors pledge $1 bn for CERN particle accelerator
Private donors pledge $1 bn for CERN particle accelerator
-
Russian court orders Austrian bank Raiffeisen to pay compensation

-
 US, Qatar, Turkey, Egypt to hold Gaza talks in Miami
US, Qatar, Turkey, Egypt to hold Gaza talks in Miami
-
Lula open to mediate between US, Venezuela to 'avoid armed conflict'

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US imposes sanctions on two more ICC judges for Israel probe

-
 US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
-
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty

-
 Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company
-
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce

-
 Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit
-
Pope replaces New York's Cardinal Dolan with pro-migrant bishop

-
 Odermatt takes foggy downhill for 50th World Cup win
Odermatt takes foggy downhill for 50th World Cup win
-
France exonerates women convicted over abortions before legalisation

-
 UK teachers to tackle misogyny in classroom
UK teachers to tackle misogyny in classroom
-
Historic Afghan cinema torn down for a mall

-
 US consumer inflation cools unexpectedly in November
US consumer inflation cools unexpectedly in November
-
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling

-
 ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future
-
Pope replaces New York's Cardinal Timothy Dolan with little-known bishop

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 Spain to buy 100 military helicopters from Airbus
Spain to buy 100 military helicopters from Airbus
-
US strike on alleged drug boat in Pacific kills four


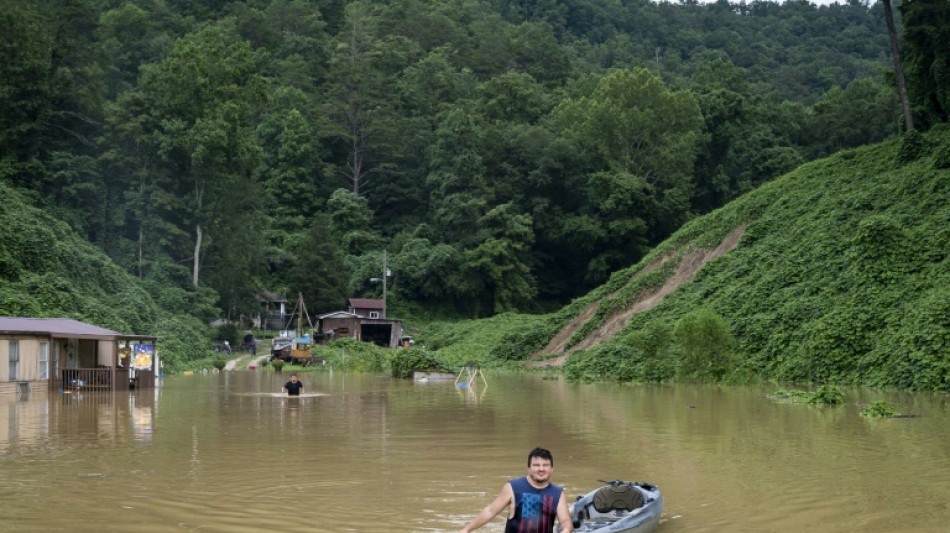
Dust to downpour: US weather whiplash shows climate change
A series of "once-in-a-millennium" rainstorms have lashed the United States in recent weeks, flooding areas baked dry by long-term droughts, as human-caused climate change brings weather whiplash.
And scientists warn that global warming means once-rare events are already much more likely, upending the models they have long used to predict possible disasters -- with worse to come.
At least 40 people have been killed in the last month by storms in Kentucky, Illinois, Texas and Missouri, inundating areas that in some cases had seen little to no rain for months.
Up to 12 inches (30 centimeters) fell in one of these storms -- the kind of downpour that statistical models say should only happen once in a thousand years.
"This is 'weather whiplash'," tweeted Peter Gleick, co-founder of the Pacific Institute, a non-governmental organization that works on water issues around the world.
It is "caused by an intensification of the global hydrological cycle & how it distributes water around the planet, influenced by human-caused climate change."
The warnings scientists have been sounding for decades about the effects of unchecked fossil fuel use are suddenly coming into focus for millions of people.
A warming planet is not a benign place in a far-off future where it is always a bit sunnier; it's a place of wild swings, where the wets are wetter and the dries are drier. And it's now.
"The commonality between these and other extreme rainfall events is you need just the right set of ingredients to come together," said David Novak, director of the Weather Prediction Center at the National Weather Service.
"You need moisture, you need instability in the atmosphere. And you need some sort of... feature to kind of ignite the storms."
While a rainstorm in Texas or Kentucky or Illinois is not unheard of at this time of year, these events were supercharged by an oversupply of atmospheric moisture -- a direct consequence of the planet being hotter.
"There's scientific consensus absolutely on the fact that warmer air can hold more moisture," Novak told AFP.
"There is more moisture available... for these fronts to tap, and so you can get these really intense rainfall events."
The science is uncontroversial -- if a little complicated for those not familiar with linear equations and difficult-to-pronounce chemistry.
The Clausius–Clapeyron equation shows that for every one degree celsius (1.8 F) the air warms, it can hold seven percent more moisture.
That's what makes hot, equatorial places noticeably more humid than cooler climes, says Novak.
And it's also what's messing with the statistics and making the one-in-1,000-year storms -- like the five that hit the US in the last month -- a lot more common.
Storms like these had a 0.1 percent chance of occurring in any given year in pre-industrial conditions, meaning that on average they would happen once every 1,000 years.
But their percentage chance of happening in a warmer environment that holds more moisture rises dramatically.
In other words, the recurrence interval -- the periods expected between these once relatively rare events -- is shrinking.
"Something that really wasn't very likely at all, just a little bit more moisture can make that quite a bit more likely," said Novak.
O.Bulka--BTB



